Noticias
Can Otter and ChatGPT produce a good-enough account of a podcast interview? – Media Nation
Published
1 año agoon


This post will no doubt have limited appeal, but a few readers might find it interesting. I’ve been thinking about how to produce summaries and news stories based on the podcast that Ellen Clegg and I host, “What Works: The Future of Local News.” The best way would be to pay a student to write it up. But is it also a task that could be turned over to AI?
Purely as an experiment, I took our most recent podcast — an interview with Scott Brodbeck, founder and CEO of Local News Now, in the Virginia suburbs of Washington, D.C. — and turned it over to the robots.
I started by downloading the audio and feeding it into Otter, a web-based transcription service that uses AI to guess at what the speaker might actually be saying. Once I had a transcript, I took a part of it — our conversation with Brodbeck, eliminating the introduction and other features — and fed it into ChatGPT twice, once asking it to produce a 600-word summary and then again to produce a 600-word news story. Important caveat: I did very little to clean up the transcript and did not edit what ChatGPT spit out.
The results were pretty good. I’m guessing it would have been better if I had been using a paid version of ChatGPT, but that would require, you know, money. I’d say that what AI produced would be publishable if some human-powered editing were employed to fix it up. Anyway, here are the results.
The transcript
Q: Scott, so many of the projects that we have looked at are nonprofit, and that trend seems to be accelerating. In fact, we love nonprofit news, but we also worry that there are limits to how much community journalism can be supported by philanthropy. So your project is for profit. How have you made that work? Dan, do you think for profit? Digital only, local news can thrive in other parts of the country as well.
A: I’m agnostic in terms of the future of both business models. I think there are nonprofits doing absolutely fantastic work. I think there are for profits that are doing great work in serving their communities. It is largely a business model distinction, and the thing that the nonprofit lets you do is raise some of that those larger philanthropic dollars or go after large donors in a community block club Chicago is one of the local operations that I respect the most. They’re amazing. The way they do their fundraising and the editorial output and how they serve their readers, absolutely amazing, and that works for them. But if I were to take the same model and try to apply it in Arlington, I don’t necessarily think it would work. It’s a smaller community. The donors who might get excited about serving Chicago, as you know, a city might. There’s just going to be a lot fewer of them, if I’m just talking about Arlington County, here, outside of DC. So for us, the for profit works we’ve had been fortunate to get lots of advertising support from local businesses. We do have some memberships, but it’s less than 10% of our revenue, maybe even less than 5% even with a recent influx when we put out the call. It’s meaningful, but it’s far from the main source of support for. Business model, and that’s what works here each community. What I’ve learned over time, because I’ve looked at potentially expanding to other other areas in years past, for the record, we are pretty firmly ensconced here in the DC area for now, but when I’ve looked at that the difference in each community and just the dynamics, and are you going to get support from advertisers? Are you going to get support from donors or philanthropy. It’s different. This is going back to local. Doesn’t scale. It’s very hard to take what works in one area and just clone, stamp it and apply it somewhere else. That’s a long way of saying that. I think both of these types of models are going to going to coexist, and they’re going to do there’s probably advantages and disadvantages, but as long as you’re serving your readers and as long as you have a viable business or a viable organization in terms of your financials, I think that’s great. I think all should be supported all the above.
Q: When we had Howard Owens of the Batavian on the podcast, he told us that he thinks for profits can actually act more independently than nonprofits, because it’s less harmful to offend one advertiser out of many than to offend one major funder who might be crucial to the whole enterprise. Do you agree with his take?
A: You know, I do, and it’s, I think it’s more of a question of revenue diversification for us. No one advertiser has more than 1% of our revenue as a result. I that’s not something I have to care about. Is what a specific advertiser thinks of a specific, you know, type of coverage we’re doing. We just, we call our own shots and approach, you know, our news coverage the way we we want to do it, without regard of what anybody external thinks. That’s the way to go here. That’s the way you serve readers, is by being independent and being a authentic voice for the community, and not being beholden to what a, you know, specific large donor thinks. Now on the nonprofit side, you know, if they’re relatively, you know, well diversified in terms of no one philanthropy or no one large donor holds too much sway, then I very much think they could be independent. But you know, if there is a situation where a particular nonprofit has a dependency on a single source, you know, I do think that calls into question, to what degree is that affecting editorial judgment? You know, not necessarily a bad thing, but I do think that, you know, you can make ask some questions there about how that’s affecting things.
Q: Scott, I’m looking at your video feed, and that is one of the most impressive mics I’ve ever seen in my life. And it leads me to think that there must be some multimedia aspects to what you’re doing that I’m not aware of. So could you talk about that a little bit?
A: We’ve tried some podcasts here and there. Over the years, there have been two main attempts at making it work. And you know, I think what we’ve found is that for us, what we have done in the past, or newsmaker interviews. We’ve also done a just kind of news discussion amongst some of our journalists, and we found an audience, but it wasn’t a it wasn’t a large audience in relation to our overall readership on the site. You know one thing about local is, especially when you’re online, only is, you are limited. You are limited in what you can do and what your resources are, and you know how much time you can spend on things. And we just ended up, after the last attempt, sunsetted the podcast. Now I the feeds are live. We could bring it back, but in the end, I decided to that we should prioritize reporting, you know, and telling stories that are of relevance to the community. So I still like multimedia. We’re going to try we’re going to be trying some stuff. We’ve been trying some stuff on social media, multimedia wise, we are going to be trying some new things, hopefully in the months to come. I do think that experimentation is important. Try things, see what works, but also don’t be afraid to make the decision if it’s not working, to pull back on it and reprioritize.
Q: Now in looking at one of your sites, ARL, now I see a pretty eclectic mix of pose it’s laid out like an old school blog in reverse chronological order. When I was looking the other day, I saw a restaurant opening an update on towing regulations, a morning Notes feature that aggregates content from other sites, some sponsored content police news and a high school football game. So what makes a local news now? Story are you are you seeking to be the news source of record in the towns that you’re in, or are you a supplement to something else?
A: I think we are. I think we are the most comprehensive local news outlets for each of the communities we serve here in Northern Virginia, and that is certainly the goal within the bounds of the resource. As we have available to us at this point, we have a newsroom of nine in the office behind me. We have about four people who work three days a week, but everybody else is remote. So newsroom is taken as a more conceptual term here. But yeah, we so it’s essentially about three people per community, and we are able to do a lot of coverage because we are able to focus, you know, our energy on reporting, and we don’t have to lay out a paper. We have a lot of automations on the back end of our of our systems where, you know, for social media, the social media posts go out automatically. Nobody has to do that. The newsletter goes out automatically. And so our reporters and editors are able to focus on just reporting the news, breaking stories you know that are of relevance to people in our community, doing the kind of service journalism around everything from what restaurant is opening down the street to, you know, where can I go and buy Christmas trees this year? We try to do everything that anybody in the community might want to know about, or at least, you know, a critical mass of people in the community might want to know about. And this approach, where you kind of mix some of the hard news, the government reporting, the elections, with what some might see as softer news. You know, local business, restaurant openings, development is in there somewhere, policing, public safety. This approach, I see it more and more working in different communities. You know, rough draft Atlanta, community impact in Texas, a number of online those are all kind of digital. You have the paper and the website. I kind of consider them peers and like minded in terms of the approach of coverage to coverage. And you see it elsewhere, with online only outlets. You know, it’s not the only model out there, but for serving a community like ours, which our communities are essentially sub markets of the DC metro area, I think it works pretty well.
Q: Your towns are pretty large, and yet, even so, I have to say three people per community sounds like a luxury in this day.
A: And we achieved this level of staffing thanks to an acquisition. We just acquired the Gazette leader, which was the weekly newspaper serving Arlington County and Fairfax County. So I before, I referenced a newspaper that was only going to the the more well, to do parts of town, and that was the sun Gazette, which was later supplanted by the Gazette leader. We were able to acquire it and the core news team of a news editor and a sports editor, which has really enhanced our coverage since that acquisition. This has been a dream to get to this level. And I do think three people, while by newsrooms, of your standards, might not seem like a lot for a place that would otherwise be served by, you know, a weekly paper. I think we are able to have a lot of impact locally and do a lot of really great reporting and telling stories that would otherwise go untold.
Q: Well, you jumped the gun on the GazetteLeader. So let me ask you about that. Back in September, you acquired a print newspaper, converted it to digital only and said you would be expanding coverage. In fact, you quoted me when I was looking at your website, I did not see the GazetteLeader listed as one of your offerings.
A: What’s going on with that is the print paper has gotten more expensive to print and produce and to distribute, rather at the same time, there’s been softening of demand for print advertising, as I understand it now, it still works in many communities, but for whatever reason, it wasn’t working here. So as a result, this was not a we just acquired the assets, the digital assets, of the Z leader, and we’re able to hire over the team, which is fantastic for our coverage, but it does mean that, unfortunately, it’s no longer in print. Now, I’ve been in talks to potentially partner with someone to put out a print publication locally. I’ve been in some talks about that. It’s far from a done deal. So there might be a revival of print in some form or fashion somewhere in our coverage area down the road. We’ll have to see how that plays out. It’s not a business that I want to have to learn a lot about and get into. You know, I think the future is clearly online. And so my goal in all this has been to figure out a enduring model for online only local news. I think we’ve figured out a lot, but I don’t have all the answers, and we’re since the acquisition and some of the additional costs we took on, we’re right about at our monthly average revenue, in terms of our expenses, we need to continue to grow from a business standpoint, and that’s what I’m focused on in the months to come. None of this is easy. You know, print, online, it’s all hard.
Q: It’s definitely not easy. But my my question was, I didn’t see the GazetteLeader offered. As a digital offering, either is the coverage area that was served by the GazetteLeader still being covered by by your network?
A: So it covered there were separate additions at one point for Arlington and for Fairfax County, and it was mostly focused on specific parts of Fairfax County, as opposed to the entire county. Long story short, we we were already covering those, and so essentially, we just absorbed the staff and the reporting they were doing, which was, you know, somewhat different than ours. Scott McCaffrey, the editor, the news editor, who came over as part of the deal, he goes to, like every single government meeting there is in Arlington, Fairfax County, and now he’s doing more in Falls Church, which is a little, little tiny city in between. Before I had been content, you know, you made note of our morning notes, where we link out to other news outlets covering news of interest to Arlington and Fairfax County. We do that from from both sides, and I was content to link to his coverage for a long time, while he was doing it. And I do think it’s important to do, but I’m like, as long as Scott’s there, he’s gonna be he’s gonna be on this, like, we can link to his coverage and focus more on, you know, what we can do uniquely well. And now we have both. We have what we were doing before, and we have Scott’s coverage, which was, you know, there was some overlap, but was differentiated. We have his coverage on both our Arlington and Fairfax site. So essentially, all the journalism that they were producing that was unique to that paper, we are now doing online on our sites.
Q: I see on your website that you offer what could be called B to B services, client services to other news outlets. What can you tell us about that?
A: So this is the services that we’re providing to pop fill and to moco show. And one thing that’s pretty clear from from the 15 years of doing this is that every part of this is hard. You know, as the the news side is hard, the sales and advertising side is hard, the membership side is hard, but also the technology bit is not easy, particularly if you have a lot of readership. Now, if you, if you’re just, you know, doing 100,000 page views or less per month, then you can probably, you know, have a bog standard WordPress site on shared hosting and be fine. But our sites, you know, our Arlington site, pop, fill, moco show, they have one, one and a half to 2 million page views per month each. And at that level, you’re talking about enterprise grade hosting, you’re talking about all sorts of little problems that come up that someone needs to fix. And while local news doesn’t scale from an editorial standpoint and sometimes a business standpoint, the technology side certainly scales. And so being on the same WordPress installation, and we have our own custom built WordPress theme that is a little more chronological feed style, as opposed to the more you know, newspaper style home page that’s been in vogue for a while. Being on the same theme allows us to also find some efficiencies in terms of our sales, so that we can go to a regional advertiser and put the same ad unit or the same type of sponsored content with the same call to action button at the at the bottom on any of the sites that we serve.
600-word summary
In a recent conversation, Scott discussed the viability and challenges of for-profit digital-only local news outlets, sharing insights into his business model and how it has evolved. Scott’s project, a for-profit news outlet serving the Northern Virginia region, provides a stark contrast to the growing trend of nonprofit local journalism. While some worry about the sustainability of community journalism funded by philanthropy, Scott believes both nonprofit and for-profit models can coexist, each with their own strengths.
He emphasizes that a for-profit model works well for his community, particularly because it allows for advertising support from local businesses. Despite having some membership revenue, it is a minor part of the income stream. He notes that the dynamics of each community vary, making it difficult to replicate successful models from one area to another. A model that works in a large city like Chicago may not be feasible in a smaller town like Arlington, Virginia, where local donors and advertisers are fewer.
Scott also agrees with Howard Owens’ view that for-profit outlets can sometimes be more independent than nonprofits. He points out that, in his model, no single advertiser makes up a significant portion of the revenue, allowing the news team to operate without undue influence. While nonprofit outlets can be independent as long as they maintain revenue diversification, Scott highlights that dependence on a single donor can raise concerns about editorial independence.
Regarding multimedia efforts, Scott mentions that his team has experimented with podcasts and social media content. While they initially found success with these formats, they decided to focus on reporting, recognizing the limitations of resources in a local, digital-only newsroom. However, they continue to experiment with new formats as part of their strategy to engage their audience.
Scott’s outlet covers a broad range of local news, from restaurant openings to public safety, government meetings, and high school sports. He aims to be the most comprehensive local news source for his community, focusing on stories that are of relevance to the area. This includes a mix of hard news, community updates, and “softer” content like local events. Despite being a small team, Scott believes they have a significant impact because they focus on local reporting and use technology to streamline operations, such as automating social media posts and newsletters.
A significant recent development for Scott’s outlet was the acquisition of the Gazette Leader, a former print newspaper. After absorbing the paper’s staff and digital assets, Scott transitioned it to a fully digital operation. Although the print version was discontinued due to rising costs and declining demand for print ads, the acquired team has greatly enhanced their coverage of Arlington and Fairfax counties. Scott notes that while the Gazette Leader is no longer in print, the expanded team continues to produce local reporting for the digital platforms, filling gaps in coverage.
Scott also touched on his outlet’s B2B services, where they provide technological and advertising solutions to other local news organizations like Popville and MoCo Show. [Note: ChatGPT actually got these two names right, although “Popville” should be rendered as “PoPville.”] With each site receiving over a million page views per month, the technical demands are high, and Scott’s team has developed a custom-built WordPress theme to handle the scale. This collaboration not only enhances the editorial content across these sites but also enables efficiencies in sales and advertising, allowing regional advertisers to reach multiple local outlets through a unified platform.
Overall, Scott’s approach underscores the importance of adaptability and experimentation in the local news space. While the business of local journalism is undoubtedly challenging, he remains focused on creating a sustainable model that balances quality reporting with financial viability, leveraging both innovative technology and a strong connection to the community.
600-word news story
Local Digital News Model Finds Success Amid Nonprofit vs. For-Profit Debate
As community journalism faces financial challenges across the U.S., a growing debate between nonprofit and for-profit business models continues to shape the future of local news. Scott, the owner of a digital-only news outlet in Northern Virginia, offers a unique perspective, arguing that both models can coexist, each with distinct advantages. His outlet, which covers multiple communities in the D.C. metro area, blends news with a revenue-driven approach, demonstrating how for-profit digital journalism can thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.
While nonprofit news organizations have gained traction in recent years, especially with the backing of philanthropic donations, Scott points out that there are limits to what these sources can achieve, especially in smaller communities. His outlet, which primarily relies on local advertising, has found success by catering to a specific audience and fostering deep local engagement. “The key is understanding your community,” he says. “What works in Arlington, Virginia, won’t necessarily work in other places. That’s why for-profit can thrive in certain areas.”
Scott stresses that the for-profit model allows for greater independence in editorial decisions, citing a perspective shared by Howard Owens of The Batavian. Owens argued that for-profit outlets, with a diversified advertiser base, can maintain editorial freedom by not being beholden to large donors, a concern for nonprofit outlets reliant on a few major philanthropists. “No single advertiser represents more than 1% of our revenue,” Scott notes, explaining that this independence allows them to cover stories without external pressure.
This freedom to cover diverse topics—from hard news like local elections and government meetings to more community-centric stories like restaurant openings and high school football games—is central to Scott’s approach. His site is a digital blend of old-school blogging and comprehensive reporting. With nine full-time staffers and a dedicated crew working remotely, his outlet has managed to serve multiple Northern Virginia communities, despite having a modest newsroom by traditional standards. “We try to be the most comprehensive local news outlet we can be within our resource constraints,” Scott explains.
The outlet has expanded recently through the acquisition of the Gazette Leader, a weekly print publication. After absorbing the editorial team, Scott converted the paper’s content into a digital format, enhancing coverage of Arlington and Fairfax Counties. While the Gazette Leader is no longer printed, Scott sees the acquisition as a step forward for local digital journalism. The transition has allowed his team to bolster coverage with more in-depth reporting from veteran journalists like Scott McCaffrey, who previously covered local government meetings. This has strengthened the outlet’s position as a key player in local news.
In addition to growing coverage, Scott’s outlet offers a unique business model by providing technology services to other news outlets. With a digital infrastructure capable of handling millions of page views, the site helps smaller outlets like Popville and MoCo Show streamline their technology and advertising operations. This collaboration allows for shared advertising and technical resources, creating efficiencies for smaller outlets that might otherwise struggle with the challenges of scaling their digital operations. “As the technology side of digital journalism scales, we can pass on some of those efficiencies to others,” Scott explains.
While Scott’s outlet has proven that digital-only, for-profit local news can succeed, he remains cautious about the future. He is keenly aware of the financial hurdles facing the industry, especially after the costs of acquiring the Gazette Leader. Despite this, he maintains that both nonprofit and for-profit outlets play essential roles in serving their communities. “The most important thing is to keep experimenting, adapting, and making sure you’re meeting the needs of your readers,” he says.
In an era where local news outlets are disappearing, Scott’s model offers a potential path forward, demonstrating that while the challenges are significant, innovation and community focus can still make local, for-profit digital journalism a viable and impactful business.
Like this:
Like Loading…
Discover more from Media Nation
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
You may like
Noticias
Revivir el compromiso en el aula de español: un desafío musical con chatgpt – enfoque de la facultad
Published
8 meses agoon
6 junio, 2025
A mitad del semestre, no es raro notar un cambio en los niveles de energía de sus alumnos (Baghurst y Kelley, 2013; Kumari et al., 2021). El entusiasmo inicial por aprender un idioma extranjero puede disminuir a medida que otros cursos con tareas exigentes compitan por su atención. Algunos estudiantes priorizan las materias que perciben como más directamente vinculadas a su especialidad o carrera, mientras que otros simplemente sienten el peso del agotamiento de mediados de semestre. En la primavera, los largos meses de invierno pueden aumentar esta fatiga, lo que hace que sea aún más difícil mantener a los estudiantes comprometidos (Rohan y Sigmon, 2000).
Este es el momento en que un instructor de idiomas debe pivotar, cambiando la dinámica del aula para reavivar la curiosidad y la motivación. Aunque los instructores se esfuerzan por incorporar actividades que se adapten a los cinco estilos de aprendizaje preferidos (Felder y Henriques, 1995)-Visual (aprendizaje a través de imágenes y comprensión espacial), auditivo (aprendizaje a través de la escucha y discusión), lectura/escritura (aprendizaje a través de interacción basada en texto), Kinesthetic (aprendizaje a través de movimiento y actividades prácticas) y multimodal (una combinación de múltiples estilos)-its is beneficiales). Estructurado y, después de un tiempo, clases predecibles con actividades que rompen el molde. La introducción de algo inesperado y diferente de la dinámica del aula establecida puede revitalizar a los estudiantes, fomentar la creatividad y mejorar su entusiasmo por el aprendizaje.
La música, en particular, ha sido durante mucho tiempo un aliado de instructores que enseñan un segundo idioma (L2), un idioma aprendido después de la lengua nativa, especialmente desde que el campo hizo la transición hacia un enfoque más comunicativo. Arraigado en la interacción y la aplicación del mundo real, el enfoque comunicativo prioriza el compromiso significativo sobre la memorización de memoria, ayudando a los estudiantes a desarrollar fluidez de formas naturales e inmersivas. La investigación ha destacado constantemente los beneficios de la música en la adquisición de L2, desde mejorar la pronunciación y las habilidades de escucha hasta mejorar la retención de vocabulario y la comprensión cultural (DeGrave, 2019; Kumar et al. 2022; Nuessel y Marshall, 2008; Vidal y Nordgren, 2024).
Sobre la base de esta tradición, la actividad que compartiremos aquí no solo incorpora música sino que también integra inteligencia artificial, agregando una nueva capa de compromiso y pensamiento crítico. Al usar la IA como herramienta en el proceso de aprendizaje, los estudiantes no solo se familiarizan con sus capacidades, sino que también desarrollan la capacidad de evaluar críticamente el contenido que genera. Este enfoque los alienta a reflexionar sobre el lenguaje, el significado y la interpretación mientras participan en el análisis de texto, la escritura creativa, la oratoria y la gamificación, todo dentro de un marco interactivo y culturalmente rico.
Descripción de la actividad: Desafío musical con Chatgpt: “Canta y descubre”
Objetivo:
Los estudiantes mejorarán su comprensión auditiva y su producción escrita en español analizando y recreando letras de canciones con la ayuda de ChatGPT. Si bien las instrucciones se presentan aquí en inglés, la actividad debe realizarse en el idioma de destino, ya sea que se enseñe el español u otro idioma.
Instrucciones:
1. Escuche y decodifique
- Divida la clase en grupos de 2-3 estudiantes.
- Elija una canción en español (por ejemplo, La Llorona por chavela vargas, Oye CÓMO VA por Tito Puente, Vivir mi Vida por Marc Anthony).
- Proporcione a cada grupo una versión incompleta de la letra con palabras faltantes.
- Los estudiantes escuchan la canción y completan los espacios en blanco.
2. Interpretar y discutir
- Dentro de sus grupos, los estudiantes analizan el significado de la canción.
- Discuten lo que creen que transmiten las letras, incluidas las emociones, los temas y cualquier referencia cultural que reconocan.
- Cada grupo comparte su interpretación con la clase.
- ¿Qué crees que la canción está tratando de comunicarse?
- ¿Qué emociones o sentimientos evocan las letras para ti?
- ¿Puedes identificar alguna referencia cultural en la canción? ¿Cómo dan forma a su significado?
- ¿Cómo influye la música (melodía, ritmo, etc.) en su interpretación de la letra?
- Cada grupo comparte su interpretación con la clase.
3. Comparar con chatgpt
- Después de formar su propio análisis, los estudiantes preguntan a Chatgpt:
- ¿Qué crees que la canción está tratando de comunicarse?
- ¿Qué emociones o sentimientos evocan las letras para ti?
- Comparan la interpretación de ChatGPT con sus propias ideas y discuten similitudes o diferencias.
4. Crea tu propio verso
- Cada grupo escribe un nuevo verso que coincide con el estilo y el ritmo de la canción.
- Pueden pedirle ayuda a ChatGPT: “Ayúdanos a escribir un nuevo verso para esta canción con el mismo estilo”.
5. Realizar y cantar
- Cada grupo presenta su nuevo verso a la clase.
- Si se sienten cómodos, pueden cantarlo usando la melodía original.
- Es beneficioso que el profesor tenga una versión de karaoke (instrumental) de la canción disponible para que las letras de los estudiantes se puedan escuchar claramente.
- Mostrar las nuevas letras en un monitor o proyector permite que otros estudiantes sigan y canten juntos, mejorando la experiencia colectiva.
6. Elección – El Grammy va a
Los estudiantes votan por diferentes categorías, incluyendo:
- Mejor adaptación
- Mejor reflexión
- Mejor rendimiento
- Mejor actitud
- Mejor colaboración
7. Reflexión final
- ¿Cuál fue la parte más desafiante de comprender la letra?
- ¿Cómo ayudó ChatGPT a interpretar la canción?
- ¿Qué nuevas palabras o expresiones aprendiste?
Pensamientos finales: música, IA y pensamiento crítico
Un desafío musical con Chatgpt: “Canta y descubre” (Desafío Musical Con Chatgpt: “Cantar y Descubrir”) es una actividad que he encontrado que es especialmente efectiva en mis cursos intermedios y avanzados. Lo uso cuando los estudiantes se sienten abrumados o distraídos, a menudo alrededor de los exámenes parciales, como una forma de ayudarlos a relajarse y reconectarse con el material. Sirve como un descanso refrescante, lo que permite a los estudiantes alejarse del estrés de las tareas y reenfocarse de una manera divertida e interactiva. Al incorporar música, creatividad y tecnología, mantenemos a los estudiantes presentes en la clase, incluso cuando todo lo demás parece exigir su atención.
Más allá de ofrecer una pausa bien merecida, esta actividad provoca discusiones atractivas sobre la interpretación del lenguaje, el contexto cultural y el papel de la IA en la educación. A medida que los estudiantes comparan sus propias interpretaciones de las letras de las canciones con las generadas por ChatGPT, comienzan a reconocer tanto el valor como las limitaciones de la IA. Estas ideas fomentan el pensamiento crítico, ayudándoles a desarrollar un enfoque más maduro de la tecnología y su impacto en su aprendizaje.
Agregar el elemento de karaoke mejora aún más la experiencia, dando a los estudiantes la oportunidad de realizar sus nuevos versos y divertirse mientras practica sus habilidades lingüísticas. Mostrar la letra en una pantalla hace que la actividad sea más inclusiva, lo que permite a todos seguirlo. Para hacerlo aún más agradable, seleccionando canciones que resuenen con los gustos de los estudiantes, ya sea un clásico como La Llorona O un éxito contemporáneo de artistas como Bad Bunny, Selena, Daddy Yankee o Karol G, hace que la actividad se sienta más personal y atractiva.
Esta actividad no se limita solo al aula. Es una gran adición a los clubes españoles o eventos especiales, donde los estudiantes pueden unirse a un amor compartido por la música mientras practican sus habilidades lingüísticas. Después de todo, ¿quién no disfruta de una buena parodia de su canción favorita?
Mezclar el aprendizaje de idiomas con música y tecnología, Desafío Musical Con Chatgpt Crea un entorno dinámico e interactivo que revitaliza a los estudiantes y profundiza su conexión con el lenguaje y el papel evolutivo de la IA. Convierte los momentos de agotamiento en oportunidades de creatividad, exploración cultural y entusiasmo renovado por el aprendizaje.
Angela Rodríguez Mooney, PhD, es profesora asistente de español y la Universidad de Mujeres de Texas.
Referencias
Baghurst, Timothy y Betty C. Kelley. “Un examen del estrés en los estudiantes universitarios en el transcurso de un semestre”. Práctica de promoción de la salud 15, no. 3 (2014): 438-447.
DeGrave, Pauline. “Música en el aula de idiomas extranjeros: cómo y por qué”. Revista de Enseñanza e Investigación de Lenguas 10, no. 3 (2019): 412-420.
Felder, Richard M. y Eunice R. Henriques. “Estilos de aprendizaje y enseñanza en la educación extranjera y de segundo idioma”. Anales de idiomas extranjeros 28, no. 1 (1995): 21-31.
Nuessel, Frank y April D. Marshall. “Prácticas y principios para involucrar a los tres modos comunicativos en español a través de canciones y música”. Hispania (2008): 139-146.
Kumar, Tribhuwan, Shamim Akhter, Mehrunnisa M. Yunus y Atefeh Shamsy. “Uso de la música y las canciones como herramientas pedagógicas en la enseñanza del inglés como contextos de idiomas extranjeros”. Education Research International 2022, no. 1 (2022): 1-9
Noticias
5 indicaciones de chatgpt que pueden ayudar a los adolescentes a lanzar una startup
Published
8 meses agoon
5 junio, 2025

Teen emprendedor que usa chatgpt para ayudarlo con su negocio
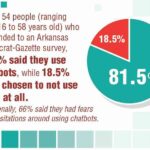
El emprendimiento adolescente sigue en aumento. Según Junior Achievement Research, el 66% de los adolescentes estadounidenses de entre 13 y 17 años dicen que es probable que considere comenzar un negocio como adultos, con el monitor de emprendimiento global 2023-2024 que encuentra que el 24% de los jóvenes de 18 a 24 años son actualmente empresarios. Estos jóvenes fundadores no son solo soñando, están construyendo empresas reales que generan ingresos y crean un impacto social, y están utilizando las indicaciones de ChatGPT para ayudarlos.
En Wit (lo que sea necesario), la organización que fundó en 2009, hemos trabajado con más de 10,000 jóvenes empresarios. Durante el año pasado, he observado un cambio en cómo los adolescentes abordan la planificación comercial. Con nuestra orientación, están utilizando herramientas de IA como ChatGPT, no como atajos, sino como socios de pensamiento estratégico para aclarar ideas, probar conceptos y acelerar la ejecución.
Los emprendedores adolescentes más exitosos han descubierto indicaciones específicas que los ayudan a pasar de una idea a otra. Estas no son sesiones genéricas de lluvia de ideas: están utilizando preguntas específicas que abordan los desafíos únicos que enfrentan los jóvenes fundadores: recursos limitados, compromisos escolares y la necesidad de demostrar sus conceptos rápidamente.
Aquí hay cinco indicaciones de ChatGPT que ayudan constantemente a los emprendedores adolescentes a construir negocios que importan.
1. El problema del primer descubrimiento chatgpt aviso
“Me doy cuenta de que [specific group of people]
luchar contra [specific problem I’ve observed]. Ayúdame a entender mejor este problema explicando: 1) por qué existe este problema, 2) qué soluciones existen actualmente y por qué son insuficientes, 3) cuánto las personas podrían pagar para resolver esto, y 4) tres formas específicas en que podría probar si este es un problema real que vale la pena resolver “.
Un adolescente podría usar este aviso después de notar que los estudiantes en la escuela luchan por pagar el almuerzo. En lugar de asumir que entienden el alcance completo, podrían pedirle a ChatGPT que investigue la deuda del almuerzo escolar como un problema sistémico. Esta investigación puede llevarlos a crear un negocio basado en productos donde los ingresos ayuden a pagar la deuda del almuerzo, lo que combina ganancias con el propósito.
Los adolescentes notan problemas de manera diferente a los adultos porque experimentan frustraciones únicas, desde los desafíos de las organizaciones escolares hasta las redes sociales hasta las preocupaciones ambientales. Según la investigación de Square sobre empresarios de la Generación de la Generación Z, el 84% planea ser dueños de negocios dentro de cinco años, lo que los convierte en candidatos ideales para las empresas de resolución de problemas.
2. El aviso de chatgpt de chatgpt de chatgpt de realidad de la realidad del recurso
“Soy [age] años con aproximadamente [dollar amount] invertir y [number] Horas por semana disponibles entre la escuela y otros compromisos. Según estas limitaciones, ¿cuáles son tres modelos de negocio que podría lanzar de manera realista este verano? Para cada opción, incluya costos de inicio, requisitos de tiempo y los primeros tres pasos para comenzar “.
Este aviso se dirige al elefante en la sala: la mayoría de los empresarios adolescentes tienen dinero y tiempo limitados. Cuando un empresario de 16 años emplea este enfoque para evaluar un concepto de negocio de tarjetas de felicitación, puede descubrir que pueden comenzar con $ 200 y escalar gradualmente. Al ser realistas sobre las limitaciones por adelantado, evitan el exceso de compromiso y pueden construir hacia objetivos de ingresos sostenibles.
Según el informe de Gen Z de Square, el 45% de los jóvenes empresarios usan sus ahorros para iniciar negocios, con el 80% de lanzamiento en línea o con un componente móvil. Estos datos respaldan la efectividad de la planificación basada en restricciones: cuando funcionan los adolescentes dentro de las limitaciones realistas, crean modelos comerciales más sostenibles.
3. El aviso de chatgpt del simulador de voz del cliente
“Actúa como un [specific demographic] Y dame comentarios honestos sobre esta idea de negocio: [describe your concept]. ¿Qué te excitaría de esto? ¿Qué preocupaciones tendrías? ¿Cuánto pagarías de manera realista? ¿Qué necesitaría cambiar para que se convierta en un cliente? “
Los empresarios adolescentes a menudo luchan con la investigación de los clientes porque no pueden encuestar fácilmente a grandes grupos o contratar firmas de investigación de mercado. Este aviso ayuda a simular los comentarios de los clientes haciendo que ChatGPT adopte personas específicas.
Un adolescente que desarrolla un podcast para atletas adolescentes podría usar este enfoque pidiéndole a ChatGPT que responda a diferentes tipos de atletas adolescentes. Esto ayuda a identificar temas de contenido que resuenan y mensajes que se sienten auténticos para el público objetivo.
El aviso funciona mejor cuando se vuelve específico sobre la demografía, los puntos débiles y los contextos. “Actúa como un estudiante de último año de secundaria que solicita a la universidad” produce mejores ideas que “actuar como un adolescente”.
4. El mensaje mínimo de diseñador de prueba viable chatgpt
“Quiero probar esta idea de negocio: [describe concept] sin gastar más de [budget amount] o más de [time commitment]. Diseñe tres experimentos simples que podría ejecutar esta semana para validar la demanda de los clientes. Para cada prueba, explique lo que aprendería, cómo medir el éxito y qué resultados indicarían que debería avanzar “.
Este aviso ayuda a los adolescentes a adoptar la metodología Lean Startup sin perderse en la jerga comercial. El enfoque en “This Week” crea urgencia y evita la planificación interminable sin acción.
Un adolescente que desea probar un concepto de línea de ropa podría usar este indicador para diseñar experimentos de validación simples, como publicar maquetas de diseño en las redes sociales para evaluar el interés, crear un formulario de Google para recolectar pedidos anticipados y pedirles a los amigos que compartan el concepto con sus redes. Estas pruebas no cuestan nada más que proporcionar datos cruciales sobre la demanda y los precios.
5. El aviso de chatgpt del generador de claridad de tono
“Convierta esta idea de negocio en una clara explicación de 60 segundos: [describe your business]. La explicación debe incluir: el problema que resuelve, su solución, a quién ayuda, por qué lo elegirían sobre las alternativas y cómo se ve el éxito. Escríbelo en lenguaje de conversación que un adolescente realmente usaría “.
La comunicación clara separa a los empresarios exitosos de aquellos con buenas ideas pero una ejecución deficiente. Este aviso ayuda a los adolescentes a destilar conceptos complejos a explicaciones convincentes que pueden usar en todas partes, desde las publicaciones en las redes sociales hasta las conversaciones con posibles mentores.
El énfasis en el “lenguaje de conversación que un adolescente realmente usaría” es importante. Muchas plantillas de lanzamiento comercial suenan artificiales cuando se entregan jóvenes fundadores. La autenticidad es más importante que la jerga corporativa.
Más allá de las indicaciones de chatgpt: estrategia de implementación
La diferencia entre los adolescentes que usan estas indicaciones de manera efectiva y aquellos que no se reducen a seguir. ChatGPT proporciona dirección, pero la acción crea resultados.
Los jóvenes empresarios más exitosos con los que trabajo usan estas indicaciones como puntos de partida, no de punto final. Toman las sugerencias generadas por IA e inmediatamente las prueban en el mundo real. Llaman a clientes potenciales, crean prototipos simples e iteran en función de los comentarios reales.
Investigaciones recientes de Junior Achievement muestran que el 69% de los adolescentes tienen ideas de negocios, pero se sienten inciertos sobre el proceso de partida, con el miedo a que el fracaso sea la principal preocupación para el 67% de los posibles empresarios adolescentes. Estas indicaciones abordan esa incertidumbre al desactivar los conceptos abstractos en los próximos pasos concretos.
La imagen más grande
Los emprendedores adolescentes que utilizan herramientas de IA como ChatGPT representan un cambio en cómo está ocurriendo la educación empresarial. Según la investigación mundial de monitores empresariales, los jóvenes empresarios tienen 1,6 veces más probabilidades que los adultos de querer comenzar un negocio, y son particularmente activos en la tecnología, la alimentación y las bebidas, la moda y los sectores de entretenimiento. En lugar de esperar clases de emprendimiento formales o programas de MBA, estos jóvenes fundadores están accediendo a herramientas de pensamiento estratégico de inmediato.
Esta tendencia se alinea con cambios más amplios en la educación y la fuerza laboral. El Foro Económico Mundial identifica la creatividad, el pensamiento crítico y la resiliencia como las principales habilidades para 2025, la capacidad de las capacidades que el espíritu empresarial desarrolla naturalmente.
Programas como WIT brindan soporte estructurado para este viaje, pero las herramientas en sí mismas se están volviendo cada vez más accesibles. Un adolescente con acceso a Internet ahora puede acceder a recursos de planificación empresarial que anteriormente estaban disponibles solo para empresarios establecidos con presupuestos significativos.
La clave es usar estas herramientas cuidadosamente. ChatGPT puede acelerar el pensamiento y proporcionar marcos, pero no puede reemplazar el arduo trabajo de construir relaciones, crear productos y servir a los clientes. La mejor idea de negocio no es la más original, es la que resuelve un problema real para personas reales. Las herramientas de IA pueden ayudar a identificar esas oportunidades, pero solo la acción puede convertirlos en empresas que importan.
Noticias
Chatgpt vs. gemini: he probado ambos, y uno definitivamente es mejor
Published
8 meses agoon
5 junio, 2025
Precio
ChatGPT y Gemini tienen versiones gratuitas que limitan su acceso a características y modelos. Los planes premium para ambos también comienzan en alrededor de $ 20 por mes. Las características de chatbot, como investigaciones profundas, generación de imágenes y videos, búsqueda web y más, son similares en ChatGPT y Gemini. Sin embargo, los planes de Gemini pagados también incluyen el almacenamiento en la nube de Google Drive (a partir de 2TB) y un conjunto robusto de integraciones en las aplicaciones de Google Workspace.
Los niveles de más alta gama de ChatGPT y Gemini desbloquean el aumento de los límites de uso y algunas características únicas, pero el costo mensual prohibitivo de estos planes (como $ 200 para Chatgpt Pro o $ 250 para Gemini Ai Ultra) los pone fuera del alcance de la mayoría de las personas. Las características específicas del plan Pro de ChatGPT, como el modo O1 Pro que aprovecha el poder de cálculo adicional para preguntas particularmente complicadas, no son especialmente relevantes para el consumidor promedio, por lo que no sentirá que se está perdiendo. Sin embargo, es probable que desee las características que son exclusivas del plan Ai Ultra de Gemini, como la generación de videos VEO 3.
Ganador: Géminis
Plataformas
Puede acceder a ChatGPT y Gemini en la web o a través de aplicaciones móviles (Android e iOS). ChatGPT también tiene aplicaciones de escritorio (macOS y Windows) y una extensión oficial para Google Chrome. Gemini no tiene aplicaciones de escritorio dedicadas o una extensión de Chrome, aunque se integra directamente con el navegador.
(Crédito: OpenAI/PCMAG)
Chatgpt está disponible en otros lugares, Como a través de Siri. Como se mencionó, puede acceder a Gemini en las aplicaciones de Google, como el calendario, Documento, ConducirGmail, Mapas, Mantener, FotosSábanas, y Música de YouTube. Tanto los modelos de Chatgpt como Gemini también aparecen en sitios como la perplejidad. Sin embargo, obtiene la mayor cantidad de funciones de estos chatbots en sus aplicaciones y portales web dedicados.
Las interfaces de ambos chatbots son en gran medida consistentes en todas las plataformas. Son fáciles de usar y no lo abruman con opciones y alternar. ChatGPT tiene algunas configuraciones más para jugar, como la capacidad de ajustar su personalidad, mientras que la profunda interfaz de investigación de Gemini hace un mejor uso de los bienes inmuebles de pantalla.
Ganador: empate
Modelos de IA
ChatGPT tiene dos series primarias de modelos, la serie 4 (su línea de conversación, insignia) y la Serie O (su compleja línea de razonamiento). Gemini ofrece de manera similar una serie Flash de uso general y una serie Pro para tareas más complicadas.
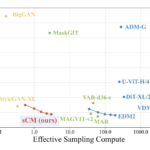
Los últimos modelos de Chatgpt son O3 y O4-Mini, y los últimos de Gemini son 2.5 Flash y 2.5 Pro. Fuera de la codificación o la resolución de una ecuación, pasará la mayor parte de su tiempo usando los modelos de la serie 4-Series y Flash. A continuación, puede ver cómo funcionan estos modelos en una variedad de tareas. Qué modelo es mejor depende realmente de lo que quieras hacer.
Ganador: empate
Búsqueda web
ChatGPT y Gemini pueden buscar información actualizada en la web con facilidad. Sin embargo, ChatGPT presenta mosaicos de artículos en la parte inferior de sus respuestas para una lectura adicional, tiene un excelente abastecimiento que facilita la vinculación de reclamos con evidencia, incluye imágenes en las respuestas cuando es relevante y, a menudo, proporciona más detalles en respuesta. Gemini no muestra nombres de fuente y títulos de artículos completos, e incluye mosaicos e imágenes de artículos solo cuando usa el modo AI de Google. El abastecimiento en este modo es aún menos robusto; Google relega las fuentes a los caretes que se pueden hacer clic que no resaltan las partes relevantes de su respuesta.
Como parte de sus experiencias de búsqueda en la web, ChatGPT y Gemini pueden ayudarlo a comprar. Si solicita consejos de compra, ambos presentan mosaicos haciendo clic en enlaces a los minoristas. Sin embargo, Gemini generalmente sugiere mejores productos y tiene una característica única en la que puede cargar una imagen tuya para probar digitalmente la ropa antes de comprar.
Ganador: chatgpt
Investigación profunda
ChatGPT y Gemini pueden generar informes que tienen docenas de páginas e incluyen más de 50 fuentes sobre cualquier tema. La mayor diferencia entre los dos se reduce al abastecimiento. Gemini a menudo cita más fuentes que CHATGPT, pero maneja el abastecimiento en informes de investigación profunda de la misma manera que lo hace en la búsqueda en modo AI, lo que significa caretas que se puede hacer clic sin destacados en el texto. Debido a que es más difícil conectar las afirmaciones en los informes de Géminis a fuentes reales, es más difícil creerles. El abastecimiento claro de ChatGPT con destacados en el texto es más fácil de confiar. Sin embargo, Gemini tiene algunas características de calidad de vida en ChatGPT, como la capacidad de exportar informes formateados correctamente a Google Docs con un solo clic. Su tono también es diferente. Los informes de ChatGPT se leen como publicaciones de foro elaboradas, mientras que los informes de Gemini se leen como documentos académicos.
Ganador: chatgpt
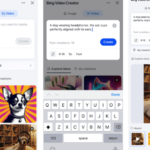
Generación de imágenes
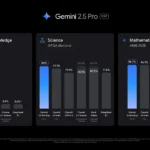
La generación de imágenes de ChatGPT impresiona independientemente de lo que solicite, incluso las indicaciones complejas para paneles o diagramas cómicos. No es perfecto, pero los errores y la distorsión son mínimos. Gemini genera imágenes visualmente atractivas más rápido que ChatGPT, pero rutinariamente incluyen errores y distorsión notables. Con indicaciones complicadas, especialmente diagramas, Gemini produjo resultados sin sentido en las pruebas.
Arriba, puede ver cómo ChatGPT (primera diapositiva) y Géminis (segunda diapositiva) les fue con el siguiente mensaje: “Genere una imagen de un estudio de moda con una decoración simple y rústica que contrasta con el espacio más agradable. Incluya un sofá marrón y paredes de ladrillo”. La imagen de ChatGPT limita los problemas al detalle fino en las hojas de sus plantas y texto en su libro, mientras que la imagen de Gemini muestra problemas más notables en su tubo de cordón y lámpara.
Ganador: chatgpt
¡Obtenga nuestras mejores historias!
Toda la última tecnología, probada por nuestros expertos
Regístrese en el boletín de informes de laboratorio para recibir las últimas revisiones de productos de PCMAG, comprar asesoramiento e ideas.
Al hacer clic en Registrarme, confirma que tiene más de 16 años y acepta nuestros Términos de uso y Política de privacidad.
¡Gracias por registrarse!
Su suscripción ha sido confirmada. ¡Esté atento a su bandeja de entrada!
Generación de videos
La generación de videos de Gemini es la mejor de su clase, especialmente porque ChatGPT no puede igualar su capacidad para producir audio acompañante. Actualmente, Google bloquea el último modelo de generación de videos de Gemini, VEO 3, detrás del costoso plan AI Ultra, pero obtienes más videos realistas que con ChatGPT. Gemini también tiene otras características que ChatGPT no, como la herramienta Flow Filmmaker, que le permite extender los clips generados y el animador AI Whisk, que le permite animar imágenes fijas. Sin embargo, tenga en cuenta que incluso con VEO 3, aún necesita generar videos varias veces para obtener un gran resultado.
En el ejemplo anterior, solicité a ChatGPT y Gemini a mostrarme un solucionador de cubos de Rubik Rubik que resuelva un cubo. La persona en el video de Géminis se ve muy bien, y el audio acompañante es competente. Al final, hay una buena atención al detalle con el marco que se desplaza, simulando la detención de una grabación de selfies. Mientras tanto, Chatgpt luchó con su cubo, distorsionándolo en gran medida.
Ganador: Géminis
Procesamiento de archivos
Comprender los archivos es una fortaleza de ChatGPT y Gemini. Ya sea que desee que respondan preguntas sobre un manual, editen un currículum o le informen algo sobre una imagen, ninguno decepciona. Sin embargo, ChatGPT tiene la ventaja sobre Gemini, ya que ofrece un reconocimiento de imagen ligeramente mejor y respuestas más detalladas cuando pregunta sobre los archivos cargados. Ambos chatbots todavía a veces inventan citas de documentos proporcionados o malinterpretan las imágenes, así que asegúrese de verificar sus resultados.
Ganador: chatgpt
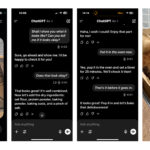
Escritura creativa
Chatgpt y Gemini pueden generar poemas, obras, historias y más competentes. CHATGPT, sin embargo, se destaca entre los dos debido a cuán únicas son sus respuestas y qué tan bien responde a las indicaciones. Las respuestas de Gemini pueden sentirse repetitivas si no calibra cuidadosamente sus solicitudes, y no siempre sigue todas las instrucciones a la carta.
En el ejemplo anterior, solicité ChatGPT (primera diapositiva) y Gemini (segunda diapositiva) con lo siguiente: “Sin hacer referencia a nada en su memoria o respuestas anteriores, quiero que me escriba un poema de verso gratuito. Preste atención especial a la capitalización, enjambment, ruptura de línea y puntuación. Dado que es un verso libre, no quiero un medidor familiar o un esquema de retiro de la rima, pero quiero que tenga un estilo de coohes. ChatGPT logró entregar lo que pedí en el aviso, y eso era distinto de las generaciones anteriores. Gemini tuvo problemas para generar un poema que incorporó cualquier cosa más allá de las comas y los períodos, y su poema anterior se lee de manera muy similar a un poema que generó antes.
Recomendado por nuestros editores
Ganador: chatgpt
Razonamiento complejo
Los modelos de razonamiento complejos de Chatgpt y Gemini pueden manejar preguntas de informática, matemáticas y física con facilidad, así como mostrar de manera competente su trabajo. En las pruebas, ChatGPT dio respuestas correctas un poco más a menudo que Gemini, pero su rendimiento es bastante similar. Ambos chatbots pueden y le darán respuestas incorrectas, por lo que verificar su trabajo aún es vital si está haciendo algo importante o tratando de aprender un concepto.
Ganador: chatgpt
Integración
ChatGPT no tiene integraciones significativas, mientras que las integraciones de Gemini son una característica definitoria. Ya sea que desee obtener ayuda para editar un ensayo en Google Docs, comparta una pestaña Chrome para hacer una pregunta, pruebe una nueva lista de reproducción de música de YouTube personalizada para su gusto o desbloquee ideas personales en Gmail, Gemini puede hacer todo y mucho más. Es difícil subestimar cuán integrales y poderosas son realmente las integraciones de Géminis.
Ganador: Géminis
Asistentes de IA
ChatGPT tiene GPT personalizados, y Gemini tiene gemas. Ambos son asistentes de IA personalizables. Tampoco es una gran actualización sobre hablar directamente con los chatbots, pero los GPT personalizados de terceros agregan una nueva funcionalidad, como el fácil acceso a Canva para editar imágenes generadas. Mientras tanto, terceros no pueden crear gemas, y no puedes compartirlas. Puede permitir que los GPT personalizados accedan a la información externa o tomen acciones externas, pero las GEM no tienen una funcionalidad similar.
Ganador: chatgpt
Contexto Windows y límites de uso
La ventana de contexto de ChatGPT sube a 128,000 tokens en sus planes de nivel superior, y todos los planes tienen límites de uso dinámicos basados en la carga del servidor. Géminis, por otro lado, tiene una ventana de contexto de 1,000,000 token. Google no está demasiado claro en los límites de uso exactos para Gemini, pero también son dinámicos dependiendo de la carga del servidor. Anecdóticamente, no pude alcanzar los límites de uso usando los planes pagados de Chatgpt o Gemini, pero es mucho más fácil hacerlo con los planes gratuitos.
Ganador: Géminis
Privacidad
La privacidad en Chatgpt y Gemini es una bolsa mixta. Ambos recopilan cantidades significativas de datos, incluidos todos sus chats, y usan esos datos para capacitar a sus modelos de IA de forma predeterminada. Sin embargo, ambos le dan la opción de apagar el entrenamiento. Google al menos no recopila y usa datos de Gemini para fines de capacitación en aplicaciones de espacio de trabajo, como Gmail, de forma predeterminada. ChatGPT y Gemini también prometen no vender sus datos o usarlos para la orientación de anuncios, pero Google y OpenAI tienen historias sórdidas cuando se trata de hacks, filtraciones y diversos fechorías digitales, por lo que recomiendo no compartir nada demasiado sensible.
Ganador: empate
Related posts










































































































































































































































































































Trending
-
 Startups2 años ago
Startups2 años agoRemove.bg: La Revolución en la Edición de Imágenes que Debes Conocer
-

 Tutoriales2 años ago
Tutoriales2 años agoCómo Comenzar a Utilizar ChatGPT: Una Guía Completa para Principiantes
-

 Startups2 años ago
Startups2 años agoStartups de IA en EE.UU. que han recaudado más de $100M en 2024
-

 Startups2 años ago
Startups2 años agoDeepgram: Revolucionando el Reconocimiento de Voz con IA
-

 Recursos2 años ago
Recursos2 años agoCómo Empezar con Popai.pro: Tu Espacio Personal de IA – Guía Completa, Instalación, Versiones y Precios
-

 Recursos2 años ago
Recursos2 años agoPerplexity aplicado al Marketing Digital y Estrategias SEO
-

 Estudiar IA2 años ago
Estudiar IA2 años agoCurso de Inteligencia Artificial Aplicada de 4Geeks Academy 2024
-

 Estudiar IA2 años ago
Estudiar IA2 años agoCurso de Inteligencia Artificial de UC Berkeley estratégico para negocios