Noticias
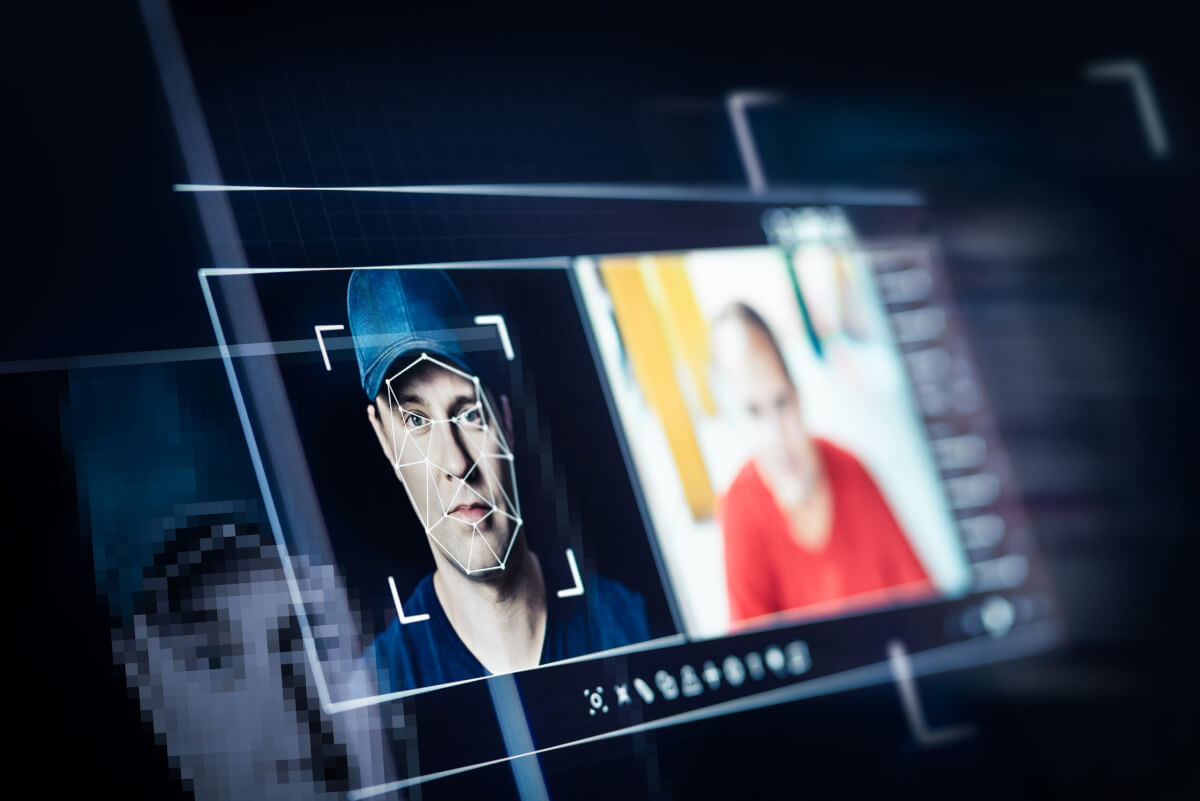
My comparison of Meta AI vs. ChatGPT vs. Google Gemini – which AI is right for you?
AI chatbots are everywhere. Whether scrolling through social media, searching for information in your Gmail, or trying to automate tasks, you’ve likely come across at least one of the big three: Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini (formerly Bard). These AI models, backed by some of the biggest names in tech, are shaping how we interact with artificial intelligence.
It all started when ChatGPT launched in November 2022, kicking off a generative AI race. Suddenly, AI wasn’t just for tech enthusiasts, it was accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
Not long after, Google introduced Gemini in March 2023, and Meta AI entered the scene in September 2023, escalating the competition. In just a short time, these AI models have evolved at breakneck speed, proving that the race to build the smartest chatbot is far from over.
If you’ve ever found yourself wondering, Which AI tool is the best for me?
Trust me, you’re not alone. As someone who constantly tests AI models for everything from writing and coding to brainstorming and problem-solving, I decided to pit these three against each other in a real-world comparison.
In this article, I’ll break down my experience with Meta’s AI, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, and Google’s Gemini, comparing their usability, creativity, response quality, speed, and overall effectiveness. Writer, developer, business owner, or just curious about AI, this deep dive will help you figure out which chatbot fits your needs best.
TL;DR: Key takeaways from this article
- Meta AI is deeply integrated into Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, making it ideal for social media interactions but limited for broader AI tasks.
- ChatGPT (by OpenAI) excels in natural conversation, creative writing, and coding, though free users may experience some restrictions.
- Google Gemini offers multimodal capabilities (text, image, and video processing) and deep integration with Google services, but its launch has had some bumps.
- Which one is best for you depends on your needs: Meta AI for social media, ChatGPT for general chat and content creation, and Gemini for research and multimedia tasks.
- AI is evolving rapidly. Features, pricing, and capabilities are changing all the time, so staying updated is key to finding the best fit.
What are Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini?
Before going into how these AI models perform, let’s see what they are and what they bring to the table.
Meta AI: The social media assistant
What is Meta AI?
Meta AI is Meta’s in-house AI assistant, designed to enhance user experiences across Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger. Unlike most AI chatbots that function as standalone tools, Meta AI is deeply embedded into social media and messaging platforms, making it a seamless part of everyday interactions.
Need quick responses, photo editing suggestions, or AI-generated search results?
Meta AI is built to keep you engaged without leaving Meta’s ecosystem.
How does Meta AI work?
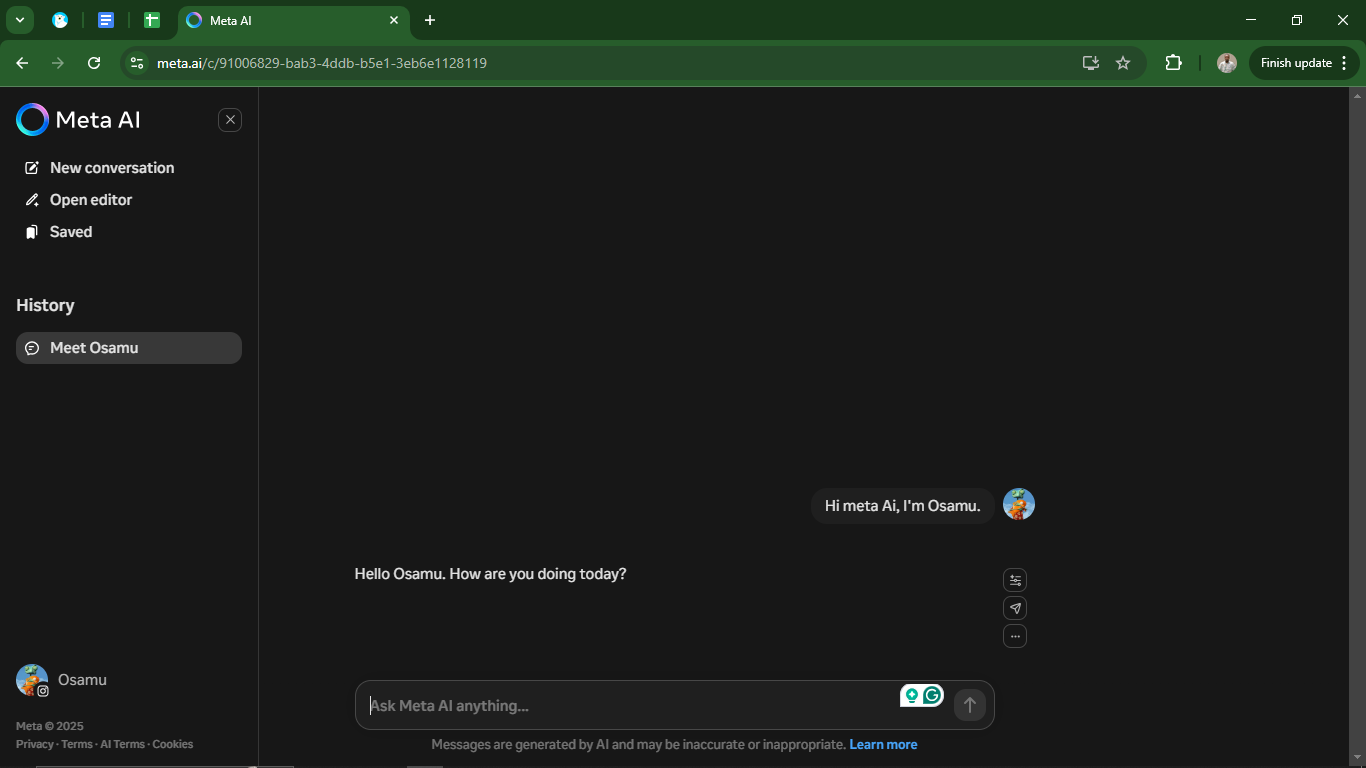
Meta AI uses large language models (LLMs) developed by Meta, allowing it to generate conversational responses, suggest content, and assist with various tasks directly within Meta’s apps. It also integrates image generation capabilities, giving users AI-powered creative tools for social media content. While it doesn’t have the same broad applications as ChatGPT or Google Gemini, it excels in social connectivity, chat automation, and engagement-driven interactions.
Meat AI at a glance
| Developer | Meta |
| Year launched | September 2023 |
| Type of AI tool | Conversational AI assistant for social media |
| Top 3 use cases | Chat automation, AI-generated search, and content suggestions |
| Who can use it? | Social media users, influencers, and digital marketers |
| Starting price | None, it’s 100% free |
| Free version | Yes |
ChatGPT: OpenAI’s all-purpose AI assistant
What is ChatGPT?
Launched by OpenAI in November 2022, ChatGPT revolutionized AI-powered content creation, automation, and productivity. If you’ve spent any time exploring AI, you’ve probably heard about ChatGPT or even used it yourself.
Unlike Meta AI, which focuses on social media interactions, ChatGPT is a versatile chatbot that helps users brainstorm ideas, summarize research, draft emails, write and debug code, and even engage in philosophical discussions. Thanks to its integration with third-party tools, it has become an essential assistant for marketers, developers, business professionals, and writers.
How does ChatGPT work?
ChatGPT is powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4o, an advanced LLM that enables it to generate human-like responses with deep contextual understanding. It leverages deep learning, reinforcement learning, and real-time web browsing to provide accurate, context-aware answers.
Unlike some competitors, ChatGPT continuously learns from user interactions, making it an adaptive AI assistant capable of handling complex problem-solving and content generation with remarkable efficiency.
ChatGPT at a glance
| Developer | OpenAI |
| Year launched | November 2022 |
| Type of AI tool | Generative AI for natural language processing |
| Top 3 use cases | Content creation, idea generation, SEO recommendations |
| Who can use it? | Marketers, content creators, bloggers, SEO professionals |
| Starting price | $20 |
| Free version | Yes, with limitations |
Google Gemini:
What is Google Gemini?
Google Gemini is Google’s response to ChatGPT, designed to integrate seamlessly with Google’s vast ecosystem. Launched in 2023, Gemini is a multimodal AI, meaning it can process text, images, audio, and even video, a major advantage over its competitors.
Unlike Meta AI, which is tied to social media, and ChatGPT, which excels in text-based (and recently audio) tasks, Gemini aims to be a jack-of-all-trades AI assistant with a focus on research, multimedia applications, and advanced problem-solving.
How does Google Gemini work?
Gemini leverages Google DeepMind’s advanced AI models, allowing it to understand and process multiple types of data simultaneously. This makes it ideal for users who need more than just text-based responses. It’s deeply integrated with Google Search, Google Docs, Gmail, and other Google services, giving it a unique edge for those already embedded in Google’s ecosystem.
While its initial release had some bumps, Google has rapidly improved Gemini, making it a strong competitor in the AI space.
Google Gemini at a glance
| Developer | Google DeepMind |
| Year launched | March 2023 |
| Type of AI tool | Multimodal AI for text, image, and video processing |
| Top 3 use cases | Research assistance, multimedia analysis, and document automation |
| Who can use it? | Students, researchers, professionals, and creatives |
| Starting price | $19.99 |
| Free version | Yes |
Why I decided to compare Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
AI tools are everywhere, but not all of them are built the same. Some specialize in social media interactions, others in deep research, and some aim to be your all-in-one AI assistant. With Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini dominating conversations, I wanted to see for myself which one delivers the best user experience.
My goal for comparing Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
This comparison isn’t just about specs and features, it’s about real-world usability. I wanted to test:
- How easy it is to sign up and start using each tool.
- The onboarding experience: do they guide new users effectively?
- How intuitive and responsive they feel right from the start.
- How do they compare to one another in different use cases?
Why does Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini matter in the first place?
LLMs like Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini are reshaping entire industries at an unimaginable pace. It doesn’t matter if you work in digital marketing, finance, legal services, or content creation, these AI tools are changing the way work gets done, quickly.
Since the launch of ChatGPT in November 2022, LLMs have:
- Boosted productivity and efficiency by providing instant access to information and automating tedious tasks.
- Unlocked new levels of creativity by generating stories, scripts, images, videos, and other content in seconds.
- Disrupted job markets, both eliminating some roles and creating entirely new career opportunities.
And from all indications, they will do even more in the future.
Getting started with Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
Meta AI: Integrated but limited
Meta AI doesn’t have a standalone app, it’s embedded directly into Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp. If you’re already using these platforms, you don’t need to sign up separately, just start chatting.
But that’s also its biggest limitation: It doesn’t feel like a fully independent AI assistant. It’s convenient for social media users but lacks the flexibility of a dedicated chatbot.
ChatGPT: A simple onboarding experience
Signing up for ChatGPT is a breeze. Head to OpenAI’s website, create an account, and you’re in. The interface is clean, distraction-free, and designed for easy access.
There’s a free version with basic features, but pro users get access to GPT-4o, which is noticeably more powerful. It offers a smooth experience on a computer or mobile device.
Google Gemini: A Google-centric AI
To use Google Gemini, you’ll need a Google account, which most people already have. It integrates directly into Google Search, Gmail, and Google Docs, making it useful for those who rely on Google’s ecosystem.
However, some of its best features are locked behind Google One subscriptions, making it less accessible to casual users.
How easy it is to get into Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
Once you’re signed up, here’s how easy it is to start using each tool:
Meta AI
Since it’s baked into Meta’s platforms, there’s zero learning curve; you just start chatting. However, it doesn’t offer as much depth as ChatGPT or Gemini, so if you’re expecting long-form content creation or advanced research, you might be underwhelmed.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is as easy as texting a friend. You type a question, and it responds. But what makes it stand out is how well it understands context and adapts to different tasks, whether you’re asking for a blog outline, Python code, or a joke about your boss.
Google Gemini
Google Gemini is powerful, but it’s Google-first integration means you need to know where to look. If you want it in Google Search, Docs, or Gmail, you’ll need to enable Gemini-powered features. It’s incredibly useful once you get the hang of it, but not as instantly intuitive as ChatGPT.
My first impression of Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
First impressions matter, especially when you’re dealing with AI models that promise to make your work easier.
Here’s how they stack up in summary:
- Meta AI is seamlessly integrated into Meta platforms, but it doesn’t feel like a standalone AI. the tool feels more like an add-on than a full-fledged AI assistant.
- ChatGPT offers the best standalone experience, with a straightforward setup and clear free vs. paid features. It’s the most user-friendly and flexible, making it a go-to for almost anything.
- Google Gemini is great for Google users, but some of its most advanced features are locked behind paywalls. It has the potential to be a research powerhouse, but its best features require some digging.
Key features comparison: Meta AI vs. ChatGPT vs. Google Gemini
AI models may all seem like magic at first glance, but under the hood, each one has its strengths, quirks, and limitations. Before we get into what makes Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini different, let’s take a moment to see what they have in common.
What do Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini have in common?
1. Multimodal capabilities (text, image, and audio)
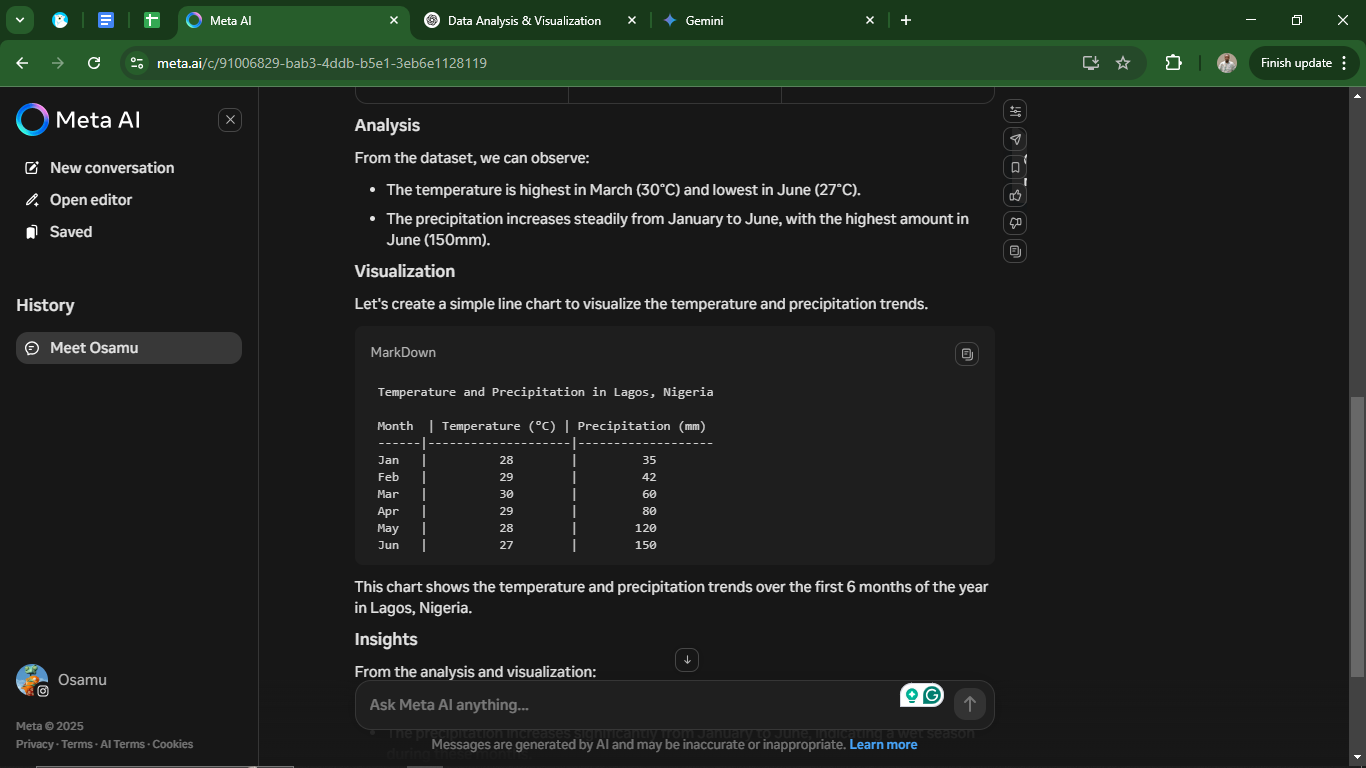
Gone are the days when AI chatbots could only generate text responses. Today, Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini all support multiple input types, meaning they can process text, images, and even audio. This allows for more dynamic interactions, such as analyzing pictures, transcribing voice commands, and generating AI-driven visuals.
However, the availability of these features varies: Gemini and ChatGPT offer real-time voice conversations across all devices, whereas Meta AI currently limits this to mobile apps.
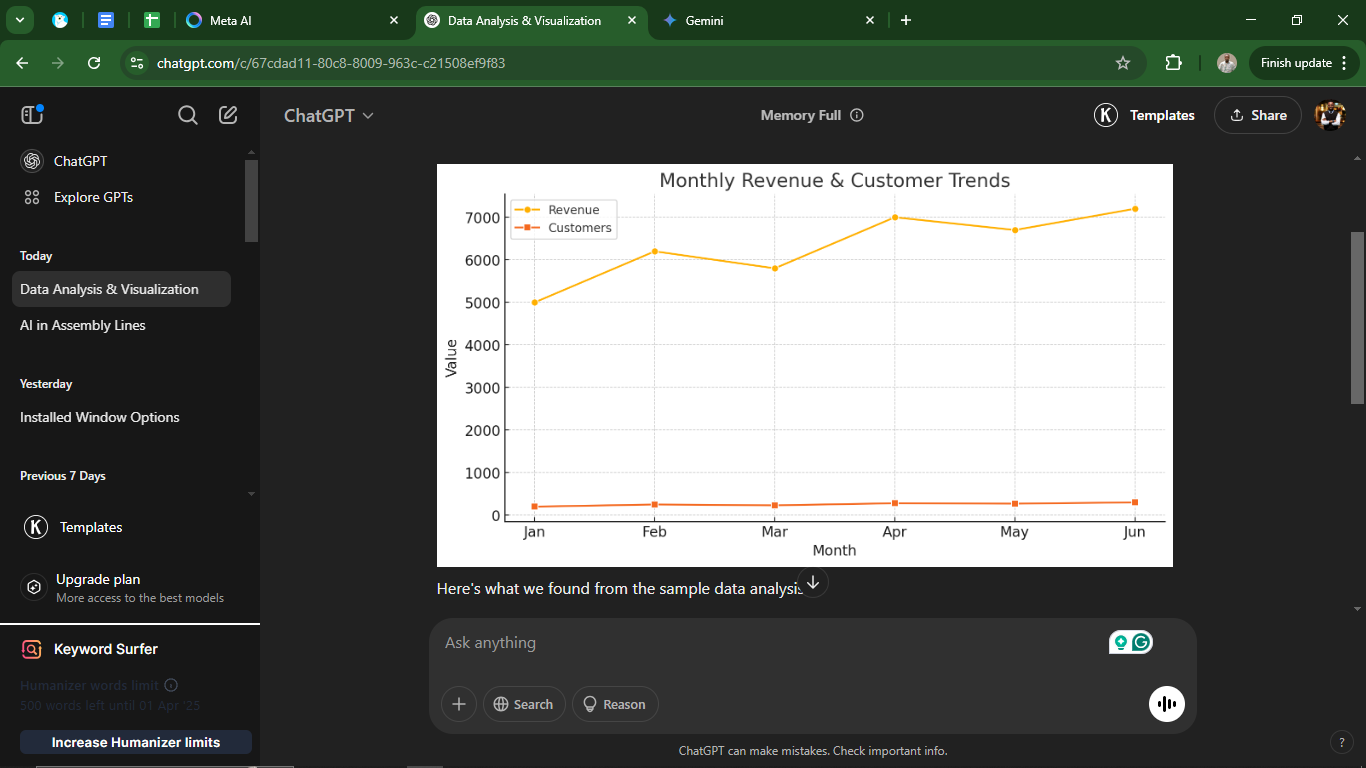
2. Data analysis
Need to break down a dataset?
Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Gemini excel at analyzing data and summarizing insights. ChatGPT and Gemini can further turn numbers into visuals and even transform information into graphs, tables, and charts. Meta AI, on the other hand, is more focused on casual interactions and social media engagement, so it doesn’t quite match the analytical depth of the other two.
3. Real-time web access
An AI model is only as good as its knowledge base, and all three chatbots offer real-time web browsing to pull the latest information. ChatGPT relies on Bing for search queries, Gemini taps into Google’s vast ecosystem, and Meta AI has access to web data, though its implementation is more geared toward social media and user-generated content.
4. Device compatibility
You can access all three AI models on both web and mobile apps, but the experience differs.
ChatGPT offers a seamless experience across browsers, mobile apps, and even a dedicated desktop application. Gemini is tightly integrated into Google’s ecosystem but lacks a desktop app. Meta AI, meanwhile, is embedded within Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, making it more of a built-in feature than a standalone AI platform.
5. Data privacy and management
Privacy-conscious users will be happy to know that all three AI models offer ways to manage conversation history. You can delete past chats, turn off memory features, and, in the case of ChatGPT, even use “temporary chats” that don’t get stored long-term. However, while ChatGPT allows you to archive past conversations, Gemini and Meta AI do not.
6. Conversation sharing
If you want to share your AI-generated conversations with others, both ChatGPT and Gemini provide options to do so. Meta AI’s sharing features are more social-media-oriented, making it easier to post AI-generated content directly to Facebook or Instagram rather than sharing entire chat histories.
How Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini differ
1. Language processing capabilities
ChatGPT is adaptive and conversational: OpenAI’s ChatGPT excels in natural language generation, producing highly coherent and human-like responses. It adapts well to different conversational styles, making it a strong choice for chatbots, virtual assistants, and general-purpose AI interactions. Its ability to remember context within conversations enhances personalization and fluidity in responses.
Google Gemini has deep language understanding: Gemini 1.5, Google’s latest AI, is trained on an extensive dataset, surpassing ChatGPT in sheer volume of words processed. Its Transformer-based neural network allows it to comprehend complex queries, deliver precise translations, and generate highly structured responses. Gemini is particularly adept at handling research-based tasks and technical inquiries.
Meta AI has open-source power: Meta’s Llama 2, a foundational open-source model, comes in various parameter sizes, with its largest model featuring 70 billion parameters. With training on 2 trillion tokens from diverse sources like Common Crawl and Wikipedia, Llama 2 delivers strong language generation but is primarily geared towards developers rather than casual users.
2. Models
Each AI has unique model strengths:
ChatGPT: Powered by GPT-4o and o1, offering models with advanced reasoning capabilities.
Google Gemini: Features multimodal capabilities with a massive one-million-token context window.
Meta AI: Uses Llama 3, optimized for open-source development.
Key differences:
- Context windows: Gemini leads with a 1 million-token window, significantly larger than ChatGPT’s 128,000 tokens.
- Logical reasoning: ChatGPT’s o1 model specializes in chain-of-thought reasoning, outperforming Gemini and Mera AI in complex problem-solving.
- Memory functionality: ChatGPT Plus includes automatic memory retention, whereas Gemini requires manual memory entries and Meata AI is available in limited countries.
| Tool | Model | Description |
| Meta AI | Llama 2 | An open-source large language model optimized for research and commercial use. It serves as the foundation for Meta’s AI initiatives, offering capabilities in natural language understanding and generation. |
| Llama 3 | The latest iteration, featuring a significantly larger 128,000-token context length and models with higher parameters, such as the 405B model. Trained on up to 15 trillion tokens, it supports up to 30 languages and offers enhanced performance.lifewire.com | |
| ChatGPT | GPT-4o | A model designed for general-purpose tasks, providing advanced language understanding and generation capabilities. |
| GPT-4o mini | A more affordable and faster variant of GPT-4o, suitable for general-purpose applications requiring quicker responses. | |
| o1 | An advanced reasoning model tailored for complex tasks, excelling in chain-of-thought reasoning and problem-solving. | |
| o1-mini | A compact version of the o1 model, ideal for complex reasoning tasks where computational efficiency is a priority. | |
| o1 Pro | The most resource-intensive model, offering superior performance for intricate tasks. Available exclusively on the $200/month ChatGPT Pro plan. | |
| Google Gemini | Gemini Nano | Optimized for devices with limited resources, this model is designed for efficient performance on smartphones, such as Samsung Galaxy S24 and Pixel devices. |
| Gemini Pro | The standard version is suitable for a wide range of applications, offering robust AI capabilities for general use. | |
| Gemini Ultra | Designed for solving complex tasks, this model is available through Gemini Advanced for private users in chatbot and Workspace apps, or via the Workspace Business package. It offers enhanced capabilities for demanding applications. |
6. Pricing
Meta AI pricing
Meta AI is 100% free
ChatGPT pricing
| Plan | Features | Cost |
| Free | Access to GPT‑4o miniReal-time web searchLimited access to GPT‑4o and o3‑miniLimited file uploads, data analysis, image generation, and voice modeCustom GPTs | $0/month |
| Plus | Everything in Free, plus:Extended messaging limitsAdvanced file uploads, data analysis, and image generationStandard and advanced voice modes (video and screen sharing)Access to o3‑mini, o3‑mini‑high, and o1 modelsCustom GPT creationLimited access to Sora video generation | $20/month |
| Pro | Everything in Plus, plus:Unlimited access to all reasoning models (including GPT‑4o)Advanced voice features, higher limits for video and screen sharingExclusive research preview of GPT‑4.5o1 Pro mode for high-performance tasksExpanded access to Sora video generationResearch preview of Operator (U.S. only) | $200/month |
Google Gemini pricing
| Plan | Description | Price | Key Features |
| Gemini | Your personal AI assistant from Google. Chat with Gemini to supercharge your ideas. | $0/month | – Access to 2.0 Flash model & 2.0 Flash Thinking experimental model- Help with writing, planning, learning & image generation- Connect with Google apps (Maps, Flights, etc.)- Free-flowing voice conversations with Gemini Live |
| Gemini Advanced | The ultimate pass to Google’s next-gen AI, including everything in Gemini and more. | $19.99/month(First month free) | – Access to the most capable models, including 2.0 Pro- Deep Research for generating comprehensive reports- Analyze books & reports up to 1,500 pages- Create & use custom AI experts with Gems- Upload and work with code repositories- 2 TB Google One storage*- Gemini integration in Gmail, Docs, and more* (available in select languages)- NotebookLM Plus with 5x higher usage limits & premium features* |
My hands-on testing experience
I’ve spent countless hours pushing these AI assistants to their limits, testing them across various real-world scenarios that matter to everyday users.
Here’s what I discovered when comparing Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini head-to-head.
1. Content creation
When it comes to crafting compelling content, ChatGPT consistently delivered the most coherent and engaging responses in my testing. Its writing flows naturally for the most part, with strong transitions and a polished tone that requires minimal editing.
Google Gemini followed closely behind, generating well-structured content with solid factual grounding, though sometimes lacking ChatGPT’s creative flair.
Meta AI, while serviceable for basic content needs, struggled with depth and sophistication. It tends to produce shorter, more surface-level responses that often need significant enhancement.
2. Coding assistance
For developers, both ChatGPT and Google Gemini proved to be reliable coding companions. ChatGPT excels at explaining complex programming concepts and debugging issues across various languages.
Google Gemini holds a notable advantage when handling Google Cloud-specific queries, clearly benefiting from deeper integration with Google’s ecosystem. Its explanations of Google API implementations were particularly impressive.
Meta AI lags considerably in this category, offering basic code snippets and frequently missing nuances in programming best practices and lacking the depth needed for complex development questions.
3. Fact-based queries
Google Gemini shone when answering factual questions, leveraging its Google Search integration to deliver accurate, up-to-date information with remarkable consistency. This makes it my go-to for researching specific facts or statistics.
ChatGPT performed admirably here as well, especially with its web browsing capability, though I occasionally noticed minor inaccuracies that weren’t present in Gemini’s responses.
Meta AI too often provided vague or outdated information during my fact-checking tests. While it handles simple queries effectively, its knowledge base seems more limited compared to its competitors.
4. Casual conversations
For everyday chit-chat, Meta AI surprisingly offers the most natural conversational experience. It’s responsive, friendly, and perfect for light interactions, though it quickly reaches its limitations when conversations deepen.
ChatGPT strikes an excellent balance between conversational warmth and substantive responses, making it engaging across both casual and more complex discussions.
Google Gemini, while informative, occasionally felt somewhat mechanical in conversational contexts. Its responses, though comprehensive, sometimes lacked the personable quality that makes interactions feel natural.
5. Image generation
The image generation space favors ChatGPT, powered by DALL·E 3’s impressive capabilities. I was consistently amazed by its ability to transform my text descriptions into strikingly realistic and creative visuals.
For those seeking even greater creative possibilities, ChatGPT’s integration with Sora for video generation puts it in a league of its own as a multimedia creation platform.
While Meta AI and Google Gemini offer image generation features, neither matches ChatGPT’s versatility or output quality in my extensive testing.
6. Research capabilities
When conducting research for articles or projects, ChatGPT proved most valuable among the three options. Even on its free plan, ChatGPT’s web access delivers current information with reasonable reliability.
In one test, I asked each AI to identify top-performing blog topics in the beauty industry. ChatGPT not only provided a comprehensive list of this year’s popular topics but also included source links to support its findings.
Google Gemini, despite its search engine parentage, surprisingly fell short in the citations department. It offered only broad references to organizational category pages rather than specific articles. Meta AI performed averagely here too.
7. Speed and responsiveness
Meta AI delivered impressively fast responses, though this speed sometimes comes at the expense of depth and nuance in the answers provided.
ChatGPT maintained an excellent balance of speed and thoroughness, particularly with GPT-4 Turbo, which handles complex requests with impressive efficiency.
Google Gemini responded rapidly to most queries but occasionally lags when processing more intricate prompts, especially those requiring specialized knowledge synthesis.
Comparison table: Meta AI vs. ChatGPT vs. Google Gemini
| Feature | Meta AI | ChatGPT | Google Gemini |
| Output quality | Decent for casual queries, but lacks depth. | Engaging and coherent responses, great for various use cases. | Strong research capabilities, but sometimes robotic. |
| Customization | Limited customization. | Offers custom GPTs and fine-tuning options. | Allows some personalization but not as extensive as ChatGPT. |
| Speed | Fast but simplistic responses. | Quick and detailed, especially with GPT-4 Turbo. | Fast but may lag on complex queries. |
| Best for | Casual conversations and quick answers. | Well-rounded AI for content, coding, and research. | Research-driven tasks and fact-based queries. |
| Free version | Free access on Meta platforms. | Yes, but with limitations. | Free access with limitations. |
| Starting price | Free. | $20/month | $19.99/month |
What I liked about each AI model
After extensive testing across different use cases, I’ve identified the standout strengths of each AI assistant.
Here’s what impressed me most about Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini during my evaluation.
Meta AI
Meta AI’s greatest advantages stem from its accessibility and straightforward approach to AI interaction:
- Easily accessible within Meta platforms: I found Meta AI seamlessly integrated across Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, eliminating the need to switch between applications. This integration makes it exceptionally convenient for quick queries while using these social platforms.
- Fast, casual conversation skills: Meta AI excels at light, natural conversations that feel remarkably human-like. It responds promptly with a conversational tone that makes it perfect for quick exchanges and simple questions.
- Free to use without paywalls: Unlike its competitors, Meta AI offers its core functionality without subscription fees or usage tiers. This democratizes access to AI assistance regardless of users’ financial resources.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT distinguishes itself through its sophisticated language capabilities and creative prowess:
- Best for long-form, creative, and structured content: I consistently found ChatGPT superior for developing comprehensive articles, essays, and creative writing. It maintains coherence across lengthy outputs and produces polished, publication-ready content.
- Strong contextual memory in premium versions: The premium versions of ChatGPT demonstrate impressive ability to remember details from earlier conversations. This contextual awareness enables more cohesive, productive interactions over extended sessions.
- Excellent for brainstorming and writing: ChatGPT proved invaluable for ideation and content development. It generates varied perspectives and approaches to creative challenges, making it an exceptional collaborative partner for writers.
Google Gemini
Google Gemini’s strengths align closely with Google’s core competencies:
- Great integration with Google tools: I appreciated how Gemini works seamlessly with Google Workspace applications. This integration streamlines workflows for users already embedded in the Google ecosystem.
- Strong factual accuracy: Gemini consistently delivered precise information on factual queries. Its connection to Google Search provides it with a distinct advantage when accuracy is paramount.
- Good for research and productivity tasks: For data-driven projects and productivity enhancement, Gemini offers substantial value. It excels at synthesizing information and helping organize research findings effectively.
Where Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini fall short
Throughout my testing, I discovered notable limitations in each platform that potential users should carefully consider before committing to any single AI solution.
Meta AI
Limited depth in responses: When I pushed Meta AI beyond surface-level inquiries, its limitations became glaringly apparent. Unlike its competitors, Meta AI frequently provides shallow responses that lack nuance, critical analysis, or comprehensive explanations. For instance, when I asked it to explain some concepts, it offered only generalized statements without the substantive insights I needed for my research.
Feels more like an add-on than a full AI assistant: Meta AI feels distinctly incomplete compared to full-featured AI assistants. Throughout my testing, I couldn’t shake the impression that it functions more as a supplementary feature bolted onto existing Meta platforms rather than a purpose-built assistant.
ChatGPT
Restrictive free version: The free version of ChatGPT significantly constrains what most users can accomplish. Without upgrading to a paid subscription, you’ll encounter outdated information (with a knowledge cutoff that grows increasingly stale) and stringent usage limits that can interrupt your workflow at inopportune moments.
Over-explanation of simple questions: ChatGPT’s tendency toward comprehensiveness sometimes works against it. When I asked straightforward questions that required concise answers, it often delivered paragraph after paragraph of explanation when a single sentence would have sufficed.
Google Gemini
Performance issues with complex requests: I found Gemini often lagging behind its competitors when handling intricate, multi-faceted queries. Tasks involving multiple steps or complex reasoning often resulted in noticeably longer response times compared to ChatGPT.
Limited free tiers: Google has adopted a similar approach to OpenAI by withholding key functionality behind premium subscriptions. Features that significantly enhance Gemini’s utility require payment, creating an incomplete experience for those unwilling or unable to subscribe.
Final verdict: Which AI model stands out among Meta AI vs. ChatGPT vs. Google Gemini?
After several hours of testing these platforms across diverse scenarios, these tools reveal clear distinctions in capability and purpose. Your ideal choice ultimately depends on your specific needs and workflow patterns.
For casual AI assistance within social platforms, Meta AI is a convenient companion for quick interactions. While it lacks the depth of its competitors, its immediate accessibility within Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp makes it uniquely positioned for spontaneous assistance during social media usage.
For deep and creative content creation, ChatGPT establishes itself as the undisputed frontrunner. Its sophisticated language processing consistently delivers nuanced, well-structured content that requires minimal editing. If your work demands substantial written output with creative flair, ChatGPT will likely become an indispensable tool in your arsenal.
For research and productivity integration, Google Gemini distinguishes itself through superior factual accuracy and seamless integration with Google’s ecosystem. Throughout my testing, Gemini consistently provided more precise information on technical queries and current events. For professionals whose workflows center around research, data analysis, and Google’s productivity suite, Gemini offers compelling advantages that its competitors simply can’t match.
Conclusion
After immersing myself in these three leading AI platforms, one truth becomes abundantly clear: we’re witnessing the evolution of AI from generic tools to personalized assistants tailored to specific contexts and needs.
The most effective approach may not involve choosing just one assistant, but strategically leveraging each for their strengths. I’ve found myself naturally developing a workflow that utilizes ChatGPT for creative and long-form content, Gemini for research and Google-integrated tasks, and Meta AI for quick assistance while browsing social media.
As these platforms rapidly evolve, the distinctions between them will likely both sharpen and blur, with each refining their core competencies while expanding into new territories. The real winner here is you, in my opinion, since these AI giants compete to deliver increasingly sophisticated and helpful experiences.
The question isn’t which AI is objectively “best,” but which aligns most effectively with your unique workflow, professional demands, and personal preferences.
FAQs about Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini
Which AI is best for content creation?
ChatGPT delivers the most engaging and coherent content, making it the top choice for writers, marketers, and bloggers. Google Gemini is decent but sometimes lacks creativity, while Meta AI is more suited for casual responses than long-form content.
Can Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini browse the internet?
Yes, all three can access the web, but ChatGPT and Google Gemini offer better real-time research capabilities. Meta AI relies more on internal data and may not provide real-time sources.
Which AI is best for coding assistance?
ChatGPT and Google Gemini handle coding well, but Gemini is better for Google Cloud-specific queries. Meta AI isn’t as advanced in this area.
How do Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini compare in image generation?
ChatGPT, powered by DALL·E 3, is the best for image generation. It even allows inpainting (editing parts of an image). Meta AI and Google Gemini offer basic image generation but lack advanced creative controls.
How fast are Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini?
Meta AI is the fastest but often simplistic. ChatGPT’s GPT-4 Turbo is quick and detailed. Google Gemini is fast but can slow down on complex prompts.
How much do Meta AI, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini cost?
Meta AI is 100% free. ChatGPT offers a free version but its premium plan starts at $20 monthly. Google Gemini also has a free version, with a premium plan at $19.99.
Disclaimer!
This publication, review, or article (“Content”) is based on our independent evaluation and is subjective, reflecting our opinions, which may differ from others’ perspectives or experiences. We do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the Content and disclaim responsibility for any errors or omissions it may contain.
The information provided is not investment advice and should not be treated as such, as products or services may change after publication. By engaging with our Content, you acknowledge its subjective nature and agree not to hold us liable for any losses or damages arising from your reliance on the information provided.
Always conduct your research and consult professionals where necessary.
Noticias
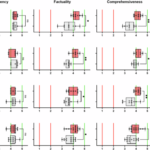
Revivir el compromiso en el aula de español: un desafío musical con chatgpt – enfoque de la facultad
Noticias
5 indicaciones de chatgpt que pueden ayudar a los adolescentes a lanzar una startup

Teen emprendedor que usa chatgpt para ayudarlo con su negocio
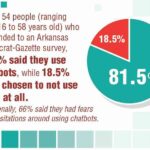
El emprendimiento adolescente sigue en aumento. Según Junior Achievement Research, el 66% de los adolescentes estadounidenses de entre 13 y 17 años dicen que es probable que considere comenzar un negocio como adultos, con el monitor de emprendimiento global 2023-2024 que encuentra que el 24% de los jóvenes de 18 a 24 años son actualmente empresarios. Estos jóvenes fundadores no son solo soñando, están construyendo empresas reales que generan ingresos y crean un impacto social, y están utilizando las indicaciones de ChatGPT para ayudarlos.
En Wit (lo que sea necesario), la organización que fundó en 2009, hemos trabajado con más de 10,000 jóvenes empresarios. Durante el año pasado, he observado un cambio en cómo los adolescentes abordan la planificación comercial. Con nuestra orientación, están utilizando herramientas de IA como ChatGPT, no como atajos, sino como socios de pensamiento estratégico para aclarar ideas, probar conceptos y acelerar la ejecución.
Los emprendedores adolescentes más exitosos han descubierto indicaciones específicas que los ayudan a pasar de una idea a otra. Estas no son sesiones genéricas de lluvia de ideas: están utilizando preguntas específicas que abordan los desafíos únicos que enfrentan los jóvenes fundadores: recursos limitados, compromisos escolares y la necesidad de demostrar sus conceptos rápidamente.
Aquí hay cinco indicaciones de ChatGPT que ayudan constantemente a los emprendedores adolescentes a construir negocios que importan.
1. El problema del primer descubrimiento chatgpt aviso
“Me doy cuenta de que [specific group of people]
luchar contra [specific problem I’ve observed]. Ayúdame a entender mejor este problema explicando: 1) por qué existe este problema, 2) qué soluciones existen actualmente y por qué son insuficientes, 3) cuánto las personas podrían pagar para resolver esto, y 4) tres formas específicas en que podría probar si este es un problema real que vale la pena resolver “.
Un adolescente podría usar este aviso después de notar que los estudiantes en la escuela luchan por pagar el almuerzo. En lugar de asumir que entienden el alcance completo, podrían pedirle a ChatGPT que investigue la deuda del almuerzo escolar como un problema sistémico. Esta investigación puede llevarlos a crear un negocio basado en productos donde los ingresos ayuden a pagar la deuda del almuerzo, lo que combina ganancias con el propósito.
Los adolescentes notan problemas de manera diferente a los adultos porque experimentan frustraciones únicas, desde los desafíos de las organizaciones escolares hasta las redes sociales hasta las preocupaciones ambientales. Según la investigación de Square sobre empresarios de la Generación de la Generación Z, el 84% planea ser dueños de negocios dentro de cinco años, lo que los convierte en candidatos ideales para las empresas de resolución de problemas.
2. El aviso de chatgpt de chatgpt de chatgpt de realidad de la realidad del recurso
“Soy [age] años con aproximadamente [dollar amount] invertir y [number] Horas por semana disponibles entre la escuela y otros compromisos. Según estas limitaciones, ¿cuáles son tres modelos de negocio que podría lanzar de manera realista este verano? Para cada opción, incluya costos de inicio, requisitos de tiempo y los primeros tres pasos para comenzar “.
Este aviso se dirige al elefante en la sala: la mayoría de los empresarios adolescentes tienen dinero y tiempo limitados. Cuando un empresario de 16 años emplea este enfoque para evaluar un concepto de negocio de tarjetas de felicitación, puede descubrir que pueden comenzar con $ 200 y escalar gradualmente. Al ser realistas sobre las limitaciones por adelantado, evitan el exceso de compromiso y pueden construir hacia objetivos de ingresos sostenibles.
Según el informe de Gen Z de Square, el 45% de los jóvenes empresarios usan sus ahorros para iniciar negocios, con el 80% de lanzamiento en línea o con un componente móvil. Estos datos respaldan la efectividad de la planificación basada en restricciones: cuando funcionan los adolescentes dentro de las limitaciones realistas, crean modelos comerciales más sostenibles.
3. El aviso de chatgpt del simulador de voz del cliente
“Actúa como un [specific demographic] Y dame comentarios honestos sobre esta idea de negocio: [describe your concept]. ¿Qué te excitaría de esto? ¿Qué preocupaciones tendrías? ¿Cuánto pagarías de manera realista? ¿Qué necesitaría cambiar para que se convierta en un cliente? “
Los empresarios adolescentes a menudo luchan con la investigación de los clientes porque no pueden encuestar fácilmente a grandes grupos o contratar firmas de investigación de mercado. Este aviso ayuda a simular los comentarios de los clientes haciendo que ChatGPT adopte personas específicas.
Un adolescente que desarrolla un podcast para atletas adolescentes podría usar este enfoque pidiéndole a ChatGPT que responda a diferentes tipos de atletas adolescentes. Esto ayuda a identificar temas de contenido que resuenan y mensajes que se sienten auténticos para el público objetivo.
El aviso funciona mejor cuando se vuelve específico sobre la demografía, los puntos débiles y los contextos. “Actúa como un estudiante de último año de secundaria que solicita a la universidad” produce mejores ideas que “actuar como un adolescente”.
4. El mensaje mínimo de diseñador de prueba viable chatgpt
“Quiero probar esta idea de negocio: [describe concept] sin gastar más de [budget amount] o más de [time commitment]. Diseñe tres experimentos simples que podría ejecutar esta semana para validar la demanda de los clientes. Para cada prueba, explique lo que aprendería, cómo medir el éxito y qué resultados indicarían que debería avanzar “.
Este aviso ayuda a los adolescentes a adoptar la metodología Lean Startup sin perderse en la jerga comercial. El enfoque en “This Week” crea urgencia y evita la planificación interminable sin acción.
Un adolescente que desea probar un concepto de línea de ropa podría usar este indicador para diseñar experimentos de validación simples, como publicar maquetas de diseño en las redes sociales para evaluar el interés, crear un formulario de Google para recolectar pedidos anticipados y pedirles a los amigos que compartan el concepto con sus redes. Estas pruebas no cuestan nada más que proporcionar datos cruciales sobre la demanda y los precios.
5. El aviso de chatgpt del generador de claridad de tono
“Convierta esta idea de negocio en una clara explicación de 60 segundos: [describe your business]. La explicación debe incluir: el problema que resuelve, su solución, a quién ayuda, por qué lo elegirían sobre las alternativas y cómo se ve el éxito. Escríbelo en lenguaje de conversación que un adolescente realmente usaría “.
La comunicación clara separa a los empresarios exitosos de aquellos con buenas ideas pero una ejecución deficiente. Este aviso ayuda a los adolescentes a destilar conceptos complejos a explicaciones convincentes que pueden usar en todas partes, desde las publicaciones en las redes sociales hasta las conversaciones con posibles mentores.
El énfasis en el “lenguaje de conversación que un adolescente realmente usaría” es importante. Muchas plantillas de lanzamiento comercial suenan artificiales cuando se entregan jóvenes fundadores. La autenticidad es más importante que la jerga corporativa.
Más allá de las indicaciones de chatgpt: estrategia de implementación
La diferencia entre los adolescentes que usan estas indicaciones de manera efectiva y aquellos que no se reducen a seguir. ChatGPT proporciona dirección, pero la acción crea resultados.
Los jóvenes empresarios más exitosos con los que trabajo usan estas indicaciones como puntos de partida, no de punto final. Toman las sugerencias generadas por IA e inmediatamente las prueban en el mundo real. Llaman a clientes potenciales, crean prototipos simples e iteran en función de los comentarios reales.
Investigaciones recientes de Junior Achievement muestran que el 69% de los adolescentes tienen ideas de negocios, pero se sienten inciertos sobre el proceso de partida, con el miedo a que el fracaso sea la principal preocupación para el 67% de los posibles empresarios adolescentes. Estas indicaciones abordan esa incertidumbre al desactivar los conceptos abstractos en los próximos pasos concretos.
La imagen más grande
Los emprendedores adolescentes que utilizan herramientas de IA como ChatGPT representan un cambio en cómo está ocurriendo la educación empresarial. Según la investigación mundial de monitores empresariales, los jóvenes empresarios tienen 1,6 veces más probabilidades que los adultos de querer comenzar un negocio, y son particularmente activos en la tecnología, la alimentación y las bebidas, la moda y los sectores de entretenimiento. En lugar de esperar clases de emprendimiento formales o programas de MBA, estos jóvenes fundadores están accediendo a herramientas de pensamiento estratégico de inmediato.
Esta tendencia se alinea con cambios más amplios en la educación y la fuerza laboral. El Foro Económico Mundial identifica la creatividad, el pensamiento crítico y la resiliencia como las principales habilidades para 2025, la capacidad de las capacidades que el espíritu empresarial desarrolla naturalmente.
Programas como WIT brindan soporte estructurado para este viaje, pero las herramientas en sí mismas se están volviendo cada vez más accesibles. Un adolescente con acceso a Internet ahora puede acceder a recursos de planificación empresarial que anteriormente estaban disponibles solo para empresarios establecidos con presupuestos significativos.
La clave es usar estas herramientas cuidadosamente. ChatGPT puede acelerar el pensamiento y proporcionar marcos, pero no puede reemplazar el arduo trabajo de construir relaciones, crear productos y servir a los clientes. La mejor idea de negocio no es la más original, es la que resuelve un problema real para personas reales. Las herramientas de IA pueden ayudar a identificar esas oportunidades, pero solo la acción puede convertirlos en empresas que importan.
Noticias
Chatgpt vs. gemini: he probado ambos, y uno definitivamente es mejor

Precio
ChatGPT y Gemini tienen versiones gratuitas que limitan su acceso a características y modelos. Los planes premium para ambos también comienzan en alrededor de $ 20 por mes. Las características de chatbot, como investigaciones profundas, generación de imágenes y videos, búsqueda web y más, son similares en ChatGPT y Gemini. Sin embargo, los planes de Gemini pagados también incluyen el almacenamiento en la nube de Google Drive (a partir de 2TB) y un conjunto robusto de integraciones en las aplicaciones de Google Workspace.
Los niveles de más alta gama de ChatGPT y Gemini desbloquean el aumento de los límites de uso y algunas características únicas, pero el costo mensual prohibitivo de estos planes (como $ 200 para Chatgpt Pro o $ 250 para Gemini Ai Ultra) los pone fuera del alcance de la mayoría de las personas. Las características específicas del plan Pro de ChatGPT, como el modo O1 Pro que aprovecha el poder de cálculo adicional para preguntas particularmente complicadas, no son especialmente relevantes para el consumidor promedio, por lo que no sentirá que se está perdiendo. Sin embargo, es probable que desee las características que son exclusivas del plan Ai Ultra de Gemini, como la generación de videos VEO 3.
Ganador: Géminis
Plataformas
Puede acceder a ChatGPT y Gemini en la web o a través de aplicaciones móviles (Android e iOS). ChatGPT también tiene aplicaciones de escritorio (macOS y Windows) y una extensión oficial para Google Chrome. Gemini no tiene aplicaciones de escritorio dedicadas o una extensión de Chrome, aunque se integra directamente con el navegador.
(Crédito: OpenAI/PCMAG)
Chatgpt está disponible en otros lugares, Como a través de Siri. Como se mencionó, puede acceder a Gemini en las aplicaciones de Google, como el calendario, Documento, ConducirGmail, Mapas, Mantener, FotosSábanas, y Música de YouTube. Tanto los modelos de Chatgpt como Gemini también aparecen en sitios como la perplejidad. Sin embargo, obtiene la mayor cantidad de funciones de estos chatbots en sus aplicaciones y portales web dedicados.
Las interfaces de ambos chatbots son en gran medida consistentes en todas las plataformas. Son fáciles de usar y no lo abruman con opciones y alternar. ChatGPT tiene algunas configuraciones más para jugar, como la capacidad de ajustar su personalidad, mientras que la profunda interfaz de investigación de Gemini hace un mejor uso de los bienes inmuebles de pantalla.
Ganador: empate
Modelos de IA
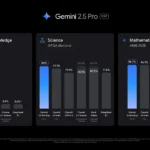
ChatGPT tiene dos series primarias de modelos, la serie 4 (su línea de conversación, insignia) y la Serie O (su compleja línea de razonamiento). Gemini ofrece de manera similar una serie Flash de uso general y una serie Pro para tareas más complicadas.
Los últimos modelos de Chatgpt son O3 y O4-Mini, y los últimos de Gemini son 2.5 Flash y 2.5 Pro. Fuera de la codificación o la resolución de una ecuación, pasará la mayor parte de su tiempo usando los modelos de la serie 4-Series y Flash. A continuación, puede ver cómo funcionan estos modelos en una variedad de tareas. Qué modelo es mejor depende realmente de lo que quieras hacer.
Ganador: empate
Búsqueda web
ChatGPT y Gemini pueden buscar información actualizada en la web con facilidad. Sin embargo, ChatGPT presenta mosaicos de artículos en la parte inferior de sus respuestas para una lectura adicional, tiene un excelente abastecimiento que facilita la vinculación de reclamos con evidencia, incluye imágenes en las respuestas cuando es relevante y, a menudo, proporciona más detalles en respuesta. Gemini no muestra nombres de fuente y títulos de artículos completos, e incluye mosaicos e imágenes de artículos solo cuando usa el modo AI de Google. El abastecimiento en este modo es aún menos robusto; Google relega las fuentes a los caretes que se pueden hacer clic que no resaltan las partes relevantes de su respuesta.
Como parte de sus experiencias de búsqueda en la web, ChatGPT y Gemini pueden ayudarlo a comprar. Si solicita consejos de compra, ambos presentan mosaicos haciendo clic en enlaces a los minoristas. Sin embargo, Gemini generalmente sugiere mejores productos y tiene una característica única en la que puede cargar una imagen tuya para probar digitalmente la ropa antes de comprar.
Ganador: chatgpt
Investigación profunda
ChatGPT y Gemini pueden generar informes que tienen docenas de páginas e incluyen más de 50 fuentes sobre cualquier tema. La mayor diferencia entre los dos se reduce al abastecimiento. Gemini a menudo cita más fuentes que CHATGPT, pero maneja el abastecimiento en informes de investigación profunda de la misma manera que lo hace en la búsqueda en modo AI, lo que significa caretas que se puede hacer clic sin destacados en el texto. Debido a que es más difícil conectar las afirmaciones en los informes de Géminis a fuentes reales, es más difícil creerles. El abastecimiento claro de ChatGPT con destacados en el texto es más fácil de confiar. Sin embargo, Gemini tiene algunas características de calidad de vida en ChatGPT, como la capacidad de exportar informes formateados correctamente a Google Docs con un solo clic. Su tono también es diferente. Los informes de ChatGPT se leen como publicaciones de foro elaboradas, mientras que los informes de Gemini se leen como documentos académicos.
Ganador: chatgpt
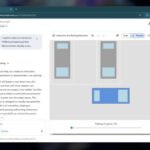
Generación de imágenes
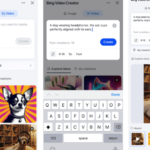
La generación de imágenes de ChatGPT impresiona independientemente de lo que solicite, incluso las indicaciones complejas para paneles o diagramas cómicos. No es perfecto, pero los errores y la distorsión son mínimos. Gemini genera imágenes visualmente atractivas más rápido que ChatGPT, pero rutinariamente incluyen errores y distorsión notables. Con indicaciones complicadas, especialmente diagramas, Gemini produjo resultados sin sentido en las pruebas.
Arriba, puede ver cómo ChatGPT (primera diapositiva) y Géminis (segunda diapositiva) les fue con el siguiente mensaje: “Genere una imagen de un estudio de moda con una decoración simple y rústica que contrasta con el espacio más agradable. Incluya un sofá marrón y paredes de ladrillo”. La imagen de ChatGPT limita los problemas al detalle fino en las hojas de sus plantas y texto en su libro, mientras que la imagen de Gemini muestra problemas más notables en su tubo de cordón y lámpara.
Ganador: chatgpt
¡Obtenga nuestras mejores historias!
Toda la última tecnología, probada por nuestros expertos
Regístrese en el boletín de informes de laboratorio para recibir las últimas revisiones de productos de PCMAG, comprar asesoramiento e ideas.
Al hacer clic en Registrarme, confirma que tiene más de 16 años y acepta nuestros Términos de uso y Política de privacidad.
¡Gracias por registrarse!
Su suscripción ha sido confirmada. ¡Esté atento a su bandeja de entrada!
Generación de videos
La generación de videos de Gemini es la mejor de su clase, especialmente porque ChatGPT no puede igualar su capacidad para producir audio acompañante. Actualmente, Google bloquea el último modelo de generación de videos de Gemini, VEO 3, detrás del costoso plan AI Ultra, pero obtienes más videos realistas que con ChatGPT. Gemini también tiene otras características que ChatGPT no, como la herramienta Flow Filmmaker, que le permite extender los clips generados y el animador AI Whisk, que le permite animar imágenes fijas. Sin embargo, tenga en cuenta que incluso con VEO 3, aún necesita generar videos varias veces para obtener un gran resultado.
En el ejemplo anterior, solicité a ChatGPT y Gemini a mostrarme un solucionador de cubos de Rubik Rubik que resuelva un cubo. La persona en el video de Géminis se ve muy bien, y el audio acompañante es competente. Al final, hay una buena atención al detalle con el marco que se desplaza, simulando la detención de una grabación de selfies. Mientras tanto, Chatgpt luchó con su cubo, distorsionándolo en gran medida.
Ganador: Géminis
Procesamiento de archivos
Comprender los archivos es una fortaleza de ChatGPT y Gemini. Ya sea que desee que respondan preguntas sobre un manual, editen un currículum o le informen algo sobre una imagen, ninguno decepciona. Sin embargo, ChatGPT tiene la ventaja sobre Gemini, ya que ofrece un reconocimiento de imagen ligeramente mejor y respuestas más detalladas cuando pregunta sobre los archivos cargados. Ambos chatbots todavía a veces inventan citas de documentos proporcionados o malinterpretan las imágenes, así que asegúrese de verificar sus resultados.
Ganador: chatgpt
Escritura creativa
Chatgpt y Gemini pueden generar poemas, obras, historias y más competentes. CHATGPT, sin embargo, se destaca entre los dos debido a cuán únicas son sus respuestas y qué tan bien responde a las indicaciones. Las respuestas de Gemini pueden sentirse repetitivas si no calibra cuidadosamente sus solicitudes, y no siempre sigue todas las instrucciones a la carta.
En el ejemplo anterior, solicité ChatGPT (primera diapositiva) y Gemini (segunda diapositiva) con lo siguiente: “Sin hacer referencia a nada en su memoria o respuestas anteriores, quiero que me escriba un poema de verso gratuito. Preste atención especial a la capitalización, enjambment, ruptura de línea y puntuación. Dado que es un verso libre, no quiero un medidor familiar o un esquema de retiro de la rima, pero quiero que tenga un estilo de coohes. ChatGPT logró entregar lo que pedí en el aviso, y eso era distinto de las generaciones anteriores. Gemini tuvo problemas para generar un poema que incorporó cualquier cosa más allá de las comas y los períodos, y su poema anterior se lee de manera muy similar a un poema que generó antes.
Recomendado por nuestros editores
Ganador: chatgpt
Razonamiento complejo
Los modelos de razonamiento complejos de Chatgpt y Gemini pueden manejar preguntas de informática, matemáticas y física con facilidad, así como mostrar de manera competente su trabajo. En las pruebas, ChatGPT dio respuestas correctas un poco más a menudo que Gemini, pero su rendimiento es bastante similar. Ambos chatbots pueden y le darán respuestas incorrectas, por lo que verificar su trabajo aún es vital si está haciendo algo importante o tratando de aprender un concepto.
Ganador: chatgpt
Integración
ChatGPT no tiene integraciones significativas, mientras que las integraciones de Gemini son una característica definitoria. Ya sea que desee obtener ayuda para editar un ensayo en Google Docs, comparta una pestaña Chrome para hacer una pregunta, pruebe una nueva lista de reproducción de música de YouTube personalizada para su gusto o desbloquee ideas personales en Gmail, Gemini puede hacer todo y mucho más. Es difícil subestimar cuán integrales y poderosas son realmente las integraciones de Géminis.
Ganador: Géminis
Asistentes de IA
ChatGPT tiene GPT personalizados, y Gemini tiene gemas. Ambos son asistentes de IA personalizables. Tampoco es una gran actualización sobre hablar directamente con los chatbots, pero los GPT personalizados de terceros agregan una nueva funcionalidad, como el fácil acceso a Canva para editar imágenes generadas. Mientras tanto, terceros no pueden crear gemas, y no puedes compartirlas. Puede permitir que los GPT personalizados accedan a la información externa o tomen acciones externas, pero las GEM no tienen una funcionalidad similar.
Ganador: chatgpt
Contexto Windows y límites de uso
La ventana de contexto de ChatGPT sube a 128,000 tokens en sus planes de nivel superior, y todos los planes tienen límites de uso dinámicos basados en la carga del servidor. Géminis, por otro lado, tiene una ventana de contexto de 1,000,000 token. Google no está demasiado claro en los límites de uso exactos para Gemini, pero también son dinámicos dependiendo de la carga del servidor. Anecdóticamente, no pude alcanzar los límites de uso usando los planes pagados de Chatgpt o Gemini, pero es mucho más fácil hacerlo con los planes gratuitos.
Ganador: Géminis
Privacidad
La privacidad en Chatgpt y Gemini es una bolsa mixta. Ambos recopilan cantidades significativas de datos, incluidos todos sus chats, y usan esos datos para capacitar a sus modelos de IA de forma predeterminada. Sin embargo, ambos le dan la opción de apagar el entrenamiento. Google al menos no recopila y usa datos de Gemini para fines de capacitación en aplicaciones de espacio de trabajo, como Gmail, de forma predeterminada. ChatGPT y Gemini también prometen no vender sus datos o usarlos para la orientación de anuncios, pero Google y OpenAI tienen historias sórdidas cuando se trata de hacks, filtraciones y diversos fechorías digitales, por lo que recomiendo no compartir nada demasiado sensible.
Ganador: empate
-
 Startups2 años ago
Startups2 años agoRemove.bg: La Revolución en la Edición de Imágenes que Debes Conocer
-

 Tutoriales2 años ago
Tutoriales2 años agoCómo Comenzar a Utilizar ChatGPT: Una Guía Completa para Principiantes
-

 Startups1 año ago
Startups1 año agoStartups de IA en EE.UU. que han recaudado más de $100M en 2024
-

 Startups2 años ago
Startups2 años agoDeepgram: Revolucionando el Reconocimiento de Voz con IA
-

 Recursos2 años ago
Recursos2 años agoCómo Empezar con Popai.pro: Tu Espacio Personal de IA – Guía Completa, Instalación, Versiones y Precios
-

 Recursos2 años ago
Recursos2 años agoPerplexity aplicado al Marketing Digital y Estrategias SEO
-

 Estudiar IA2 años ago
Estudiar IA2 años agoCurso de Inteligencia Artificial de UC Berkeley estratégico para negocios
-

 Estudiar IA2 años ago
Estudiar IA2 años agoCurso de Inteligencia Artificial Aplicada de 4Geeks Academy 2024