Claude vs ChatGPT: Which is best for your business?
There’s no doubt that OpenAI changed the game in 2022, when it introduced the first iteration of ChatGPT, and showed us all the potential of generative AI bots. ChatGPT quickly became one of the fastest-growing apps of all time, and inspired the creation of countless competing bots – including Claude, the Gen AI assistant created by Anthropic.
While ChatGPT is still arguably the more “popular” tool for most users – Claude has earned a lot of attention in recent years. Both Claude and ChatGPT now have some clear pros and cons that make the more (or less) appealing to specific users.
So, how do you make the right choice? I put both of these solutions to the test to help you make a more informed decision for your business needs.
Claude vs ChatGPT: An Overview
First, it’s worth noting that comparing any generative AI assistant can be complicated. After all, these tools evolve pretty quickly. Claude, for instance, now boasts better “cooperative skills” and capabilities for team members, since the launch of the Sonnet 3.5 model.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, now has more features for specific use cases, thanks to the launch of the o1 models (for advanced reasoning). It also has a wider range of pricing plans to choose from, including Enterprise and Team editions, as well as the new ChatGPT Pro.
Here’s a quick overview of both options, and the “models” that power them.
Introducing Claude AI: Definition and Models
Claude is the AI chatbot created by Anthropic, a startup co-founded by ex-Open AI members. What makes Claude compelling for a lot of users is that Anthropic has focused heavily on making generative AI “safe” and useful. Like ChatGPT, Claude is powered by LLMs, but it features a constitutional design that helps to minimize the risk of bias, discrimination and hallucinations.
Like ChatGPT, Claude can create content, answer questions, and even be accessed to create custom bots, thanks to Anthropic’s APIs. However, it can’t search the web, and it’s not fully “multimodal”. For instance, although Claude can analyze images, it can’t create them, like ChatGPT can with DALL-E 3. The current models available for Claude are:
- Claude Haiku: The cheapest, fastest, and most lightweight model of Claude, Haiku is available to Claude Pro and Team subscribers via the iOS app and Claude.AI. For developers, Haiku costs $0.25 per million input tokens, and $1.25 per million output tokens.
- Claude Sonnet: The best combination model for speed and efficiency, Sonnet is available to both paying Claude users, and developers. The API costs $15 per million output tokens, and $3 per million input tokens.
- Claude Opus: The most advanced and costly model, Opus is available to Pro, Team, and Enterprise users, as well as developers. For API users, Opus costs $75 per million output tokens and $15 per million input tokens.
Claude AI Pricing
I mentioned some of the pricing details for developers using Claude APIs above, but you can find the full list of costs on Anthropic’s website here. If you just want to access the Claude AI chatbot, there’s a free plan for beginners, with limited access to Claude models on the web, iOS and Android.
Paid plans start at $18 per month, per user for the “Pro” plan, which includes early access to new features, projects for organizing chats and documents, and Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Opus models. You also get better usage limits than you would on the free plan.
For business users, there’s Claude Team for $25 per user per month, with central billing and administration, as well as collaboration features. Alternatively, you can choose the custom-priced Enterprise plan for SSO, domain capture, role-based access, SCIM, data source integrations, and audit logs.
Introducing ChatGPT: Definition and Models
As you’ll see throughout this Claude vs ChatGPT comparison, there are a lot of similarities between the two bots. Both offer access to APIs, and come with multiple models to choose from. ChatGPT is a little more versatile, however. The bot, created by OpenAI was first released in 2022, and has since evolved to feature numerous models, such as:
- GPT-4: The most advanced model available for ChatGPT before the release of GPT-4o. This model is available on all plans (including the free plan). It also supports multimodal capabilities, with the ability to generate images and respond to voice.
- GPT-4o and GPT-4o Mini: The current “flagship models” for ChatGPT, GPT-4o and 4o-Mini are fast, cost effective, and multimodal. They can understand uploaded files, and generate images. Plus, users can create custom GPTs with these models.
- The o1 models: The o1 models (GPT o1, o1-mini, and o1 Pro) are the latest models created by OpenAI at the time of writing. They’re specially designed for advanced reasoning capabilities – but can’t browse the web, and are slower than the GPT-4o models.
Compared to Claude, the ChatGPT models are more flexible, with the ability to browse the internet, create different types of content (like images), and advanced API options.
ChatGPT Pricing
API pricing for OpenAI’s ChatGPT models vary by model, however it’s worth noting that you do only pay for what you use, and can get discounts if you use the Batch API. For those who just want to access ChatGPT (without any specific developer features), there are various plans available.
The free plan includes access to GPT-4o mini, standard voice model, limited access to GPT-4o, and limited file upload capabilities. You can use custom GPTs, but you won’t be able to create them. Paid plans start at $20 per month for ChatGPT Plus, with extended messaging and upload limits, advanced voice model, limited access to o1 and o1-mini models, and custom GPT creation.
For businesses, OpenAI offers the Team plan ($25 or $30 per user, per month), with more advanced features, and an admin console for workspace management. There’s also a custom Enterprise plan with high-speed access to the top models, expanded context windows, admin controls, analytics, and domain verification. Plus, OpenAI recently introduced a new plan, ChatGPT Pro, for $200 per month, per user, with advanced access to the o1 models.
Claude vs ChatGPT: Performance Results
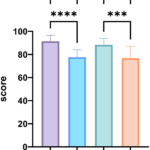
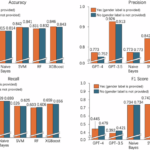
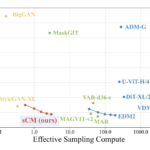
The most common way to compare models like Claude vs ChatGPT, is to use “standardized” tests. Most AI leaders share insights into the performance of their models on specific tests, like the MMLU text, which evaluates undergrade-level knowledge, or HumanEval, for coding.
The trouble is that not every AI leader uses the same tests. Even when they do embrace the same “benchmarks”, the results really only offer a limited insight into what these models can do. For instance, Anthropic published a head-to-head comparison of its Sonnet 3.5 model against other models like Llama and GPT-4o, but it really only delivers a snapshot oversight.
Many AI and machine learning experts say that this kind of testing really overstates the progress of LLMs. As new models are released, they can sometimes be trained on their own evaluation data – which means they get better at performing on standardized tests, but not better “overall”.
For a better “hands-on” understanding of how these models compare, I did my own tests, but here’s a quick run-down of the options side by side to get us started.
| Comparison | Claude | ChatGPT |
| Creator | Anthropic | OpenAI |
| Models | Claude Sonnet, Haiku, and Opus | GPT 4, GPT-4o, GPT 4o-Mini, o1, o1-mini, and o1 Pro |
| Context window | Up to 1 million for some use cases | 128,000 tokens |
| Unique features | Advanced safety features, and slightly cheaper pricing | Image generation, audio understanding, advanced reasoning (o1 models), and internet access (some models) |
| Pricing | Variable API pricing, free plan, and paid plans starting at $18 per month, per user. | Variable API pricing, free plan, and paid plans starting at $20 per month, per user. |
| File upload | Yes | Yes |
| Integrations | Yes | Yes |
Claude vs ChatGPT: Privacy, Safety and Security
As AI governance and security become more of a concern for business users, it’s becoming increasingly important for companies to consider how “safe” the models they access are.
As I mentioned above, one thing that really makes Claude stand out, is Anthropic’s approach to constitutional AI. The company pioneered the approach to training its models with foundational principles and rules that align with human values.
That doesn’t necessarily mean Claude AI will always be safer than ChatGPT, but the model does refuse to answer potentially “harmful” prompts more often. Additionally, it’s worth noting Anthropic doesn’t automatically train its models with user interactions – unless they opt in.
Alternatively, OpenAI does train its models on user interactions, unless you specifically “opt out”, or you’re using a paid business-level plan, like ChatGPT Team or Enterprise. Both companies do implement safety measures and guardrails into their models, but ChatGPT has been a little less transparent about the guardrails it uses.
Notably though, the new o1 models were trained with a new methodology that makes it more effective at mitigating “jailbreak” attempts. For instance, the o1 models scored 84 out of 100 compared to GPT-4o’s score of 22 on an advanced jailbreak test.
Claude vs ChatGPT: Creativity and Content Creation
While there are plenty of use cases for generative AI tools like Claude and ChatGPT these days – one of the most common ways to use these tools is for content creation. Both AI bots excel in this area – but in different ways. For instance, ChatGPT is the better option for diverse content creation.
Unlike Claude, ChatGPT can browse the web to source all kinds of information for up-to-date articles, reports, and other types of content. Because it can check the web for ideas, it’s also a little better at “brainstorming”, ideas for solutions to different problems.
Plus, ChatGPT can generate images, but you can only create images on a paid plan, whereas other alternatives, such as Google Gemini, allow free users to generate visual content too.
Claude AI, on the other hand, excels at “written” output in certain ways. When I asked both tools to write an introduction to an article about LLMs, ChatGPT came up with pretty generic-sounding, flowery content. We’re all tired of seeing the same phrases as “in today’s fast-moving world,” etc.
Claude created slightly more “original” sounding content. It was also very good at assessing the documents and content I uploaded. ChatGPT can do that too, but I often find the bot gets confused when it’s given too much information to review at once.
Claude is better at proof-reading too. When I asked both Claude and ChatGPT to “fix” a passage of content with obvious factual errors and misspellings, Claude identified them all. ChatGPT, on the other hand, still checked the content well, but it seemed to try and “rewrite” everything in a new tone of voice, which was something I didn’t ask it to do.
Unfortunately, since Claude can’t access the internet, it can’t “fact-check” any very recent information from the web.
Image and Content Processing Capabilities
Although Claude has fewer “multimodal” capabilities than ChatGPT – both tools can process “uploaded” content. However, there are limitations on how much information you can upload, based on the plan you choose.
I found both tools to be reasonably effective at analyzing photos, but they can only gather so much information from an image. For instance, both tools seem to struggle with “counting” the number of objects in a photo, or distinguishing the difference between similar objects (like apples and oranges).
ChatGPT is definitely better at summarizing larger documents. Although Claude can process up to 200k tokens from a document (compared to 128k for ChatGPT), GPT-4o was better at understanding the text given to it than Claude in my test.
ChatGPT does a great job of converting large pieces of text into simple summaries with clear “key points”. Claude can summarize text quite well, but it sometimes makes mistakes, like failing to count the number of times a specific word or phrase was used in a document.
Overall, I do think there are better tools out their for content summarization than both Claude and ChatGPT, however. You can find an insight into some of my top recommendations for AI summary tools (like Notta, and Hypotenuse) here.
Complex Reasoning: ChatGPT Comes Out on Top
For complex reasoning tasks (particularly those linked to math and science), ChatGPT is definitely the better tool. That’s particularly true now that we have access to the o1 models, that are specifically designed to use “chain of thought” processes to think deeper about complex tasks.
Claude isn’t really designed to think carefully about tasks, although it does respond well to questions about physics equations. ChatGPT, however, can dive a lot more deeply into questions about science, math, and finance, and deliver a lot more intuitive responses.
For instance, when I asked ChatGPT to reason through a physics problem for me, it took longer to generate a response (with the o1 model). However, it also broke the answer down into clear steps, that felt a lot easier to follow. ChatGPT also answered math questions faster with the GPT-4o model than Claude. Sometimes, Claude didn’t even bother to give a direct answer when I asked it to solve a math equation – it just told me how to figure out the answer for myself.
Both solutions do struggle a little bit with things like sentiment analysis, and solving ethical problems, however. With the o1 models, ChatGPT can provide deep insights into ethical problems (like the trolley problem), and even understand the sentiment within a conversation. Claude can understand sentiment reasonably well, but I found it delivered pretty generic responses to ethical questions.
Of course, that could have something to do with Anthropic introducing such strict guardrails to ensure that the “responses” Claude gives aren’t harmful. These guardrails could prevent the bot from generating responses that might be perceived in a certain way.
Claude vs ChatGPT: Coding Performance
I don’t know much about coding, so it was hard to fully evaluate Claude vs ChatGPT in this area. However, ChatGPT does have a great reputation for producing high-quality code. The GPT-4o model, in particular, is excellent at creating and debugging code quickly.
Additionally, the o1 models achieved brilliant results on various coding “benchmarking” tests. For instance, the o1 model achieved an 89th percentile score in a Codeforces contest. What might make Claude a little better for some coding tasks, is its unique “Artifacts” feature.
The Artifacts feature brings up a preview window for users as they write code – so you can actually see what your code will do as it works. For instance, you could use Artifacts to create characters for a video game and see how they might interact.
Since you can see the results of your code immediately, you can easily ask Claude to make changes to graphics, and specific elements. With ChatGPT, you need a lot more specific programming knowledge to really make the most of the bot’s coding capabilities.
Customization: Integrations and GPTs
One thing that makes ChatGPT a slightly more powerful option than Claude for some businesses, is the ability to create custom GPTs, and leverage a wide range of integrations. Although Claude can integrate with some apps, and enables users to create their own bot experiences through APIs, ChatGPT makes it much easier to build unique experiences with custom GPTs.
You can create your own GPTs with natural language, and add them to the GPT marketplace, where other people can access them. Anthropic doesn’t have a “GPT” equivalent, although there is a prompt library available with “optimized prompts” you can use for certain tasks, like enhancing Python code.
Neither company offers companies the ability to create “full” autonomous agents yet. However, you can create custom agents with similar functionality to ChatGPT through Microsoft Copilot Studio. Anthropic also has a solution for creating AI agents with “function calling” capabilities.
However, there are a lot of better options for autonomous agent creation available right now – such as Google’s Vertex AI system with access to Gemini 2.0, and Amazon Bedrock Studio.
Claude vs ChatGPT: Which is Better Value for Money?
Both Claude and ChatGPT have free plans for people who want to just experiment with the bot (in a limited way), without paying anything. If you’re happy to sign up for a premium plan, Claude’s paid plans are slightly cheaper – starting at $18 per month per user.
However, I do think that ChatGPT offers better value for money overall. First of all, the free plan gives you a lot more for nothing, with access to limited multimodal capabilities, advanced models, and a bot that can actually browse the internet.
Secondly, the paid plans, though slightly more expensive, allow you to do a lot more with your AI, such as creating custom GPTs, or generating images. Those are things you can’t really do on any Claude AI paid plan – no matter how much you spend.
Claude vs ChatGPT: Which is Best?
Overall, Claude and ChatGPT have a lot in common. They’re both powerful AI solutions, ideal for a wide range of tasks, ranging from text analysis, to brainstorming, and even coding.
Claude is probably the better choice if you’re concerned about AI safety, and want a little more “creativity” when you’re creating new content (Even if you can’t create images). It’s also a slightly more user-friendly solution for coding tasks, thanks to the Artifacts feature. Plus, it does feature some handy collaboration capabilities, with things like “Projects” for teams.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, is the better “jack of all trades” AI tool. It can generate text, and images, summarize content more effectively, and even deal with advanced reasoning tasks using the o1 models. Plus, it can browse the web, understand audio input, and be customized with unique GPTs, integrations, and plugins.
For most users, ChatGPT will be the better option overall. However, it’s worth remembering that both of these tools are constantly evolving. Make sure you keep an eye on our latest news stories about both Claude, and ChatGPT – you never know when one might overtake the other.